Solving Binary Optimisation Problems using a Binary Genetic Algorithm 使用二元遺傳算法解決二元優化問題
Capital budgeting/project selection problem 資本預算/項目選擇問題
A company is evaluating 4 projects which each run for 3 years and have the following characteristics. 一家公司正在評估 4 個項目,每個項目都運行 3 年,具有以下特徵。
Capital requirements (m) Project Return ($m) Year 1 2 3 1 0.2 0.5 0.3 0.2 2 0.3 1.0 0.8 0.2 3 0.5 1.5 1.5 0.3 4 0.1 0.1 0.4 0.1 Available capital ($m) 3.1 2.5 0.4 Decision problem: Which projects should be selected to maximize the total profits? 如何選擇項目以最大化總利潤?
Explanation: 解釋:
- Once a project has been selected, all yearly capital requirement (investments) must be met in full 選擇項目後,必須全額滿足所有年度資本要求(投資)
- There is a capital (budget) available for each year, that should not be exceeded 每年都有可用的資本(預算),不應超過
Problem formulation 問題公式化
- Decision variables : which project to select 決策變量:選擇哪個項目
- : project is not selected
- : project is selected
- It is essentially a 0-1 (binary) integer programming problem
- Objective: Maximize the expected returns 目標:最大化預期回報
- Constraints: Yearly budget cannot be exceeded 年度預算不得超過
- Question: The formulation above is a 0-1 integer programming problem. Do you think this kind of problems is easy to solve? Why? 上述公式化是一個 0-1 整數規劃問題。你認為這種問題是否容易解決?為什麼?
0-1 integer programming problems 0-1 整數規劃問題
0-1 integer programming is NP-complete. See Richard Karp's 21 NP-complete problems
- P vs NP vs NP-complete vs NP-hard
- P: a complexity class that represents the set of all decision problems that can be solved in polynomial time (efficiently). P:一個複雜類,表示所有可以在多項式時間內解決的決策問題的集合。
- NP: a complexity class that represents the set of all decision problems for which the instances where the answer is "yes" have proofs that can be verified in polynomial time. NP:一個複雜類,表示所有可以在多項式時間內解決的決策問題的集合。
- NP-complete: NP-Complete is a complexity class which represents the set of all problems X in NP for which it is possible to reduce any other NP problem Y to X in polynomial time. NP-complete:NP-Complete 是一個複雜類,表示 NP 中所有問題 X 的集合,對於這些問題,可以在多項式時間內將任何其他 NP 問題 Y 簡化為 X。
- Intuition: NP-complete means we can solve Y quickly if we know how to solve X quickly. NP-complete 意味著如果我們知道如何快速解決 X,則可以快速解決 Y。
- P vs NP vs NP-complete vs NP-hard
- P versus NP problem: an 1-million dollar open question to ask whether "polynomial time algorithms actually exist for solving NP-Complete, or NP problems?" Current answer is NO. P 與 NP 問題:一個 1 百萬美元的開放問題,問題是"多項式時間算法是否真的存在,用於解決 NP-Complete 或 NP 問題?"當前答案是 NO。
- NP-Hard: the problems that are at least as hard as the NP-complete problems. NP-Hard:至少與 NP-complete 問題一樣難的問題。
- Note: NP-hard problems do not have to be in NP, and they do not have to be decision problems. 注意:NP-hard 問題不一定是 NP 問題,也不一定是決策問題。
How to solve the problem
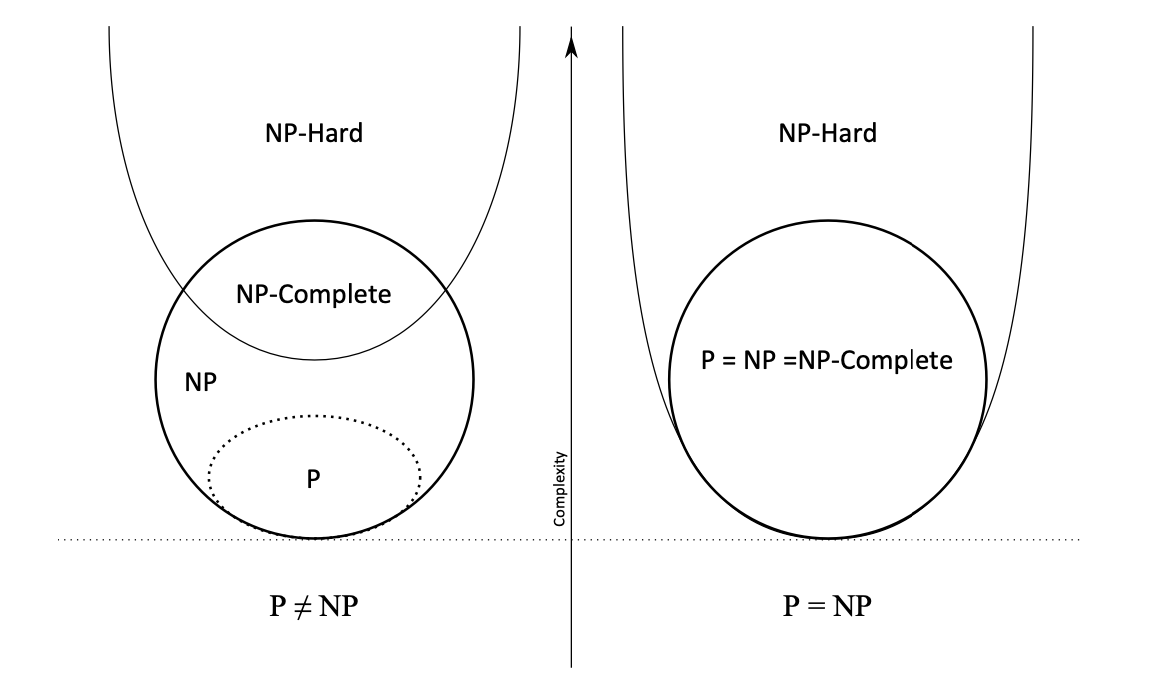
Figure 1: Euler diagram for P, NP, NP-complete, and NP-hard set of problems. From Wikipedia
- Deterministic (Exact) methods:
- The Branch & Bound Method: Relax the problem as a continuous problem 分支定界法:將問題放鬆為連續問題
- Heuristic methods: 進化算法
- Local search (hill climbing) 局部搜索(爬山)
- Simulated Annealing (SA) 模擬退火
- Genetic Algorithm (GA) 進化算法
Generic Evolutionary Algorithm 通用進化算法

Building blocks of Evolutionary Algorithms 進化算法的構建塊
- An Evolutionary Algorithms consists of: 一個進化算法由以下組成:
- representation: each solution is called an individual 表示:每個解決方案稱為一個個體
- fitness (objective) function: to evaluate solutions 適應度(目標)函數:評估解決方案
- variation operators: mutation and crossover 變異算子:突變和交叉
- selection and reproduction : survival of the fittest 選擇和繁殖:適者生存
Genetic Representation: general principle 一般原則
- The selection of representation depends on the problem to be solved. 選擇表示取決於要解決的問題。
- We have the following choices:
- Binary representation 二進制表示
- Real number representation 實數表示
- Random key representation 隨機鍵表示
- Other problem specific representations 其他特定問題的表示
Exercise: BGA for project selection problem 用 BGA 解決專案選擇問題
- Open my BGA_template.m file
- Understand the fitness calculation function 理解適應度計算函數
- Complete the following sections: 完成以下部分:
- Initialisation 初始化
- Crossover 交叉
- Mutation 突變
- Run you algorithm 30 times and record the average results and standard deviation. 重複運行 30 次,並記錄平均結果和標準差。
Exercise: Project selection problem extensions 專案選擇問題的擴展
- A new scenario: 一個新的情況:
- If project 1 finishes in year 2, and all of the return from project 1 is available as capital in year 3 如果專案 1 在第 2 年完成,並且專案 1 的所有收益都在第 3 年作為資本可用
- Projects 1 and 2 are mutually exclusive 專案 1 和 2 互斥
- How to model this problem? 如何建模這個問題?
Exercise: Project selection problem extensions 專案選擇問題的擴展
Solution:
- If project 1 finishes in year 2, and all of the return from project 1 is available as capital in year 3, then this can be formulated by changing the capital requirement constraint for year 3 to: 如果專案 1 在第 2 年完成,並且專案 1 的所有收益都在第 3 年作為資本可用,則可以通過將第 3 年的資本需求約束更改為:
or equivalently: 或等價於:
- However, we also need to change the objective function to count the return from the project. Question: How to do this? 然而,我們還需要更改目標函數以計算專案的收益。問題:如何做到這一點?
- Projects 1 and 2 are mutually exclusive:
Please read Prof. J E Beasley's OR-Notes on Integer Programming
Extra exercise
- Use your implemented Binary GA to solvethe office assignment problem