Stochastic Local Search algorithms 隨機局部搜索算法
Let's take a look at some simple examples 讓我們看一些簡單的例子
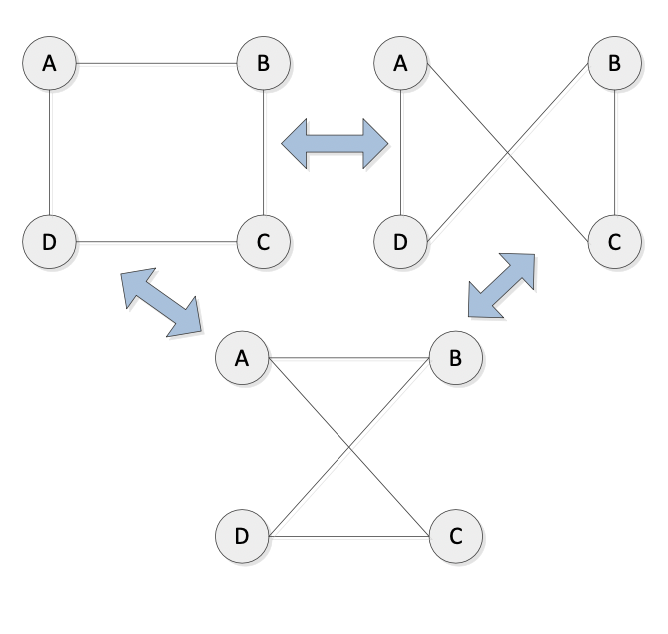
- 2-3 cities: only one solutions 2-3 個城市:只有一個解決方案
- 4 cities: 3 solutions 4 個城市:3 個解決方案
- Question: How those tours of the 4 cities TSP differ? 這些 4 個城市 TSP 的旅行路線有什麼不同?
- Answer (Observation): two immediate neighbour solutions can be two routes (cycles) only differ from two edges 一個解決方案與它的鄰居解決方案只有兩個邊不同
- Idea: Swapping two edges results in an immediate neighbour solution 交換兩個邊可以得到一個鄰居解決方案
2-Opt algorithm 2-Opt 算法
- Question: Given a route,e.g.,A−→C−→B−→D−→A, how to swap two edges? 給定一個路線,如何交換兩個邊?
- Note: if you can answer this question, you invent 2-Opt algorithm, a famous local search operator first proposed by Croes in 1958 [1] for solving the travelling salesman problem. 這個問題的答案就是 2-Opt 算法,這是一個用來解決旅行推銷員問題的著名的局部搜索算子,由 Croes 在 1958 年提出。
- Detailed swapping steps for swapping two edges, which result in an immediate neighbour solutions: 交換兩個邊的詳細步驟,這將產生一個鄰居解決方案:
- Step 1: removal of two edges from the current route, which results in two parts of the route. 從當前路線中刪除兩個邊,這將產生兩個部分的路線
- Step 2: reconnect by two other edges to obtain a new solution 通過另外兩個邊重新連接以獲得新的解決方案
Suppose we have a route: A−→C−→B−→D−→A, let's see how to swap: 假設我們有一個路線:A−→C−→B−→D−→A,讓我們看看如何交換兩個邊:
Step 1: removal of two edges from the current route, which results in two parts of the route 從當前路線中刪除兩個邊,這將產生兩個部分的路線
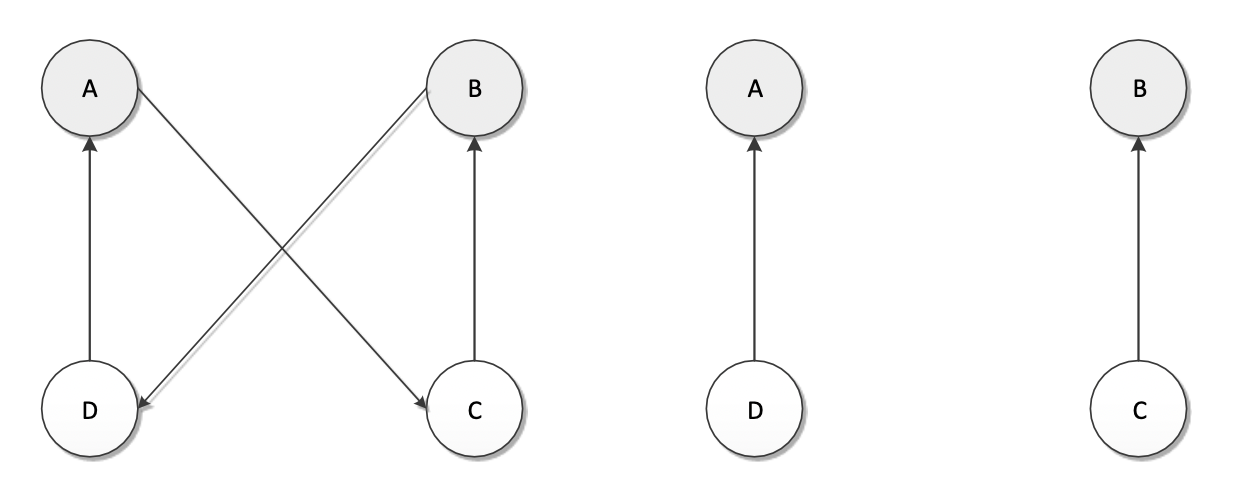
Step 2: reconnect by two other edges to obtain a new solution. 通過另外兩個邊重新連接以獲得新的解決方案
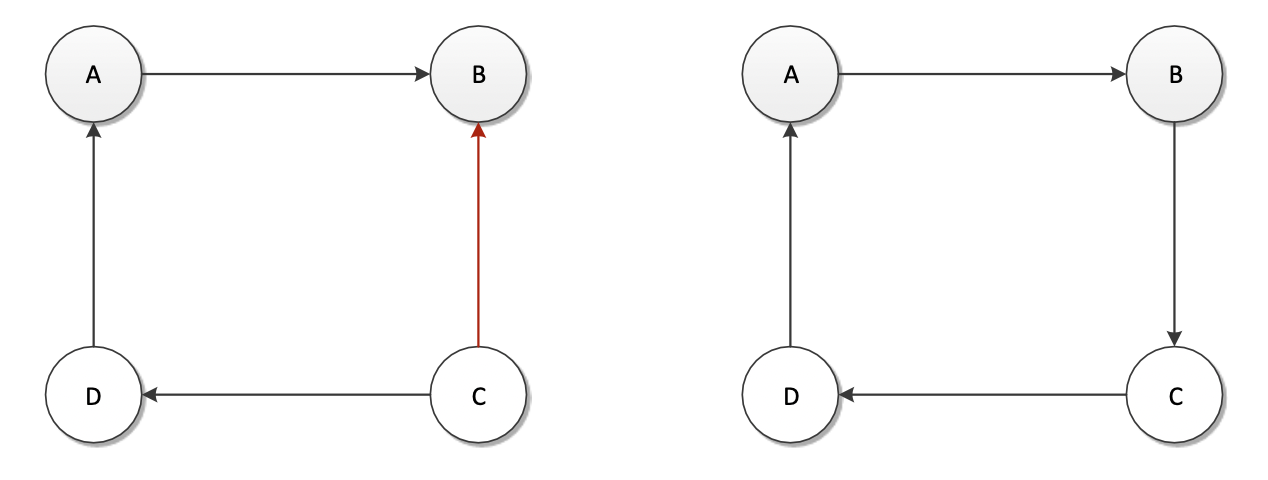
We need to reverse the order of one part of the solution, e.g., C −→ B in order to get an optimal route: A−→B−→C−→D−→A 我們需要反轉解決方案的一部分的順序,例如 C −→ B 以獲得最佳路線:A−→B−→C−→D−→A
2-Opt algorithm for 6 cities TSP 6 個城市 TSP 的 2-Opt 算法
Suppose we have a route: A−→B−→C−→D−→E−→F−→A, let's see how to swap: 假設我們有一個路線:A−→B−→C−→D−→E−→F−→A,讓我們看看如何交換兩個邊:
Step 1: removal of two edges from the current route, which results in two parts of the tour 從當前路線中刪除兩個邊,這將產生兩個部分的路線
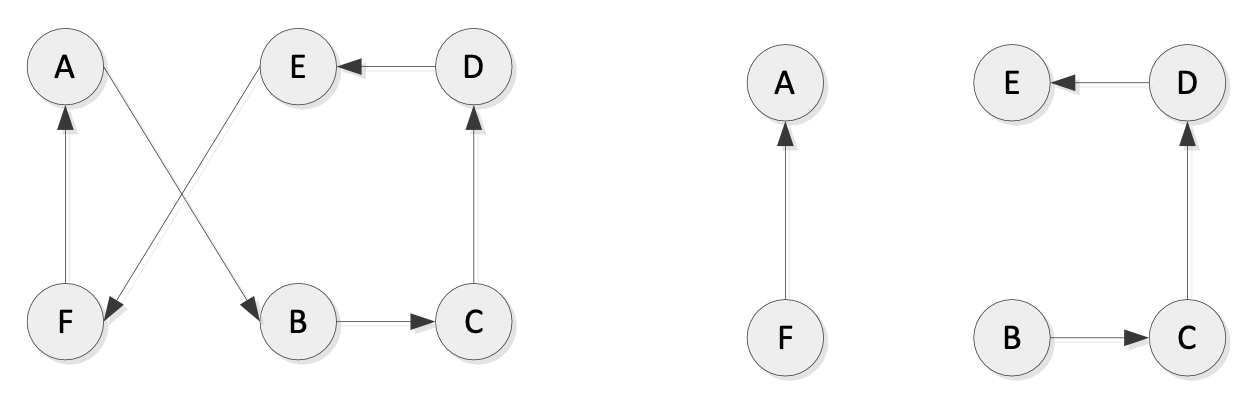
Step 2: reconnect by two other edges to obtain a new solution 通過另外兩個邊重新連接以獲得新的解決方案
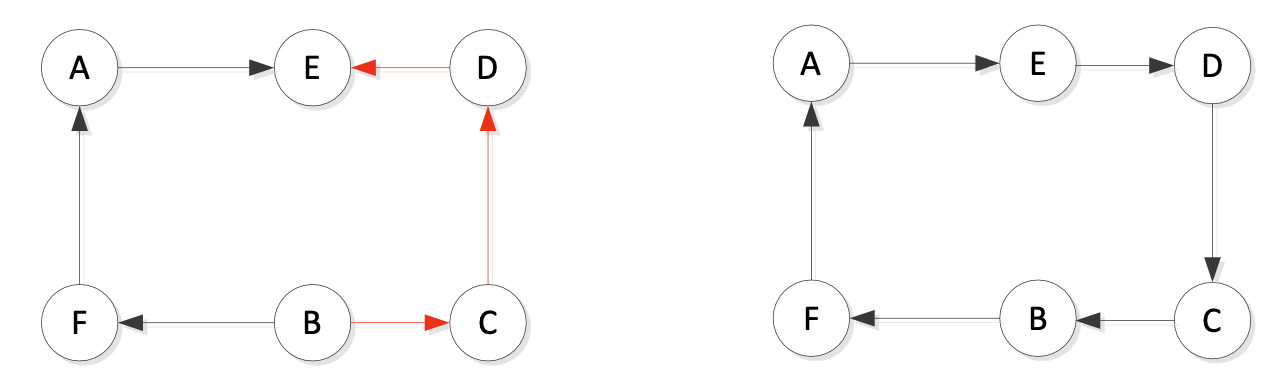
We need to reverse the order of B ⇐ C ⇐ D ⇐ E in order to get A −→ E −→ D −→ C −→ B −→ F −→ A 我們需要反轉解決方案的一部分的順序,例如 B ⇐ C ⇐ D ⇐ E 以獲得最佳路線:A −→ E −→ D −→ C −→ B −→ F −→ A
2-Opt algorithm: implementation 2-Opt 算法:實現
We observed 2-Opt essentially swap two cities, e.g., in the 6 cities TSP, 2-Opt swaps B and E. We therefore have the following algorithm: 我們觀察到 2-Opt 本質上是交換兩個城市,例如,在 6 個城市 TSP 中,2-Opt 交換 B 和 E。因此我們有以下算法:

Fitness landscape with global/local optima 有全局/局部最優解的適應度景觀
Fitness landscape of a 1-dimensional optimisation problem with global and local optima: 一維優化問題的適應度景觀,有全局和局部最優解:
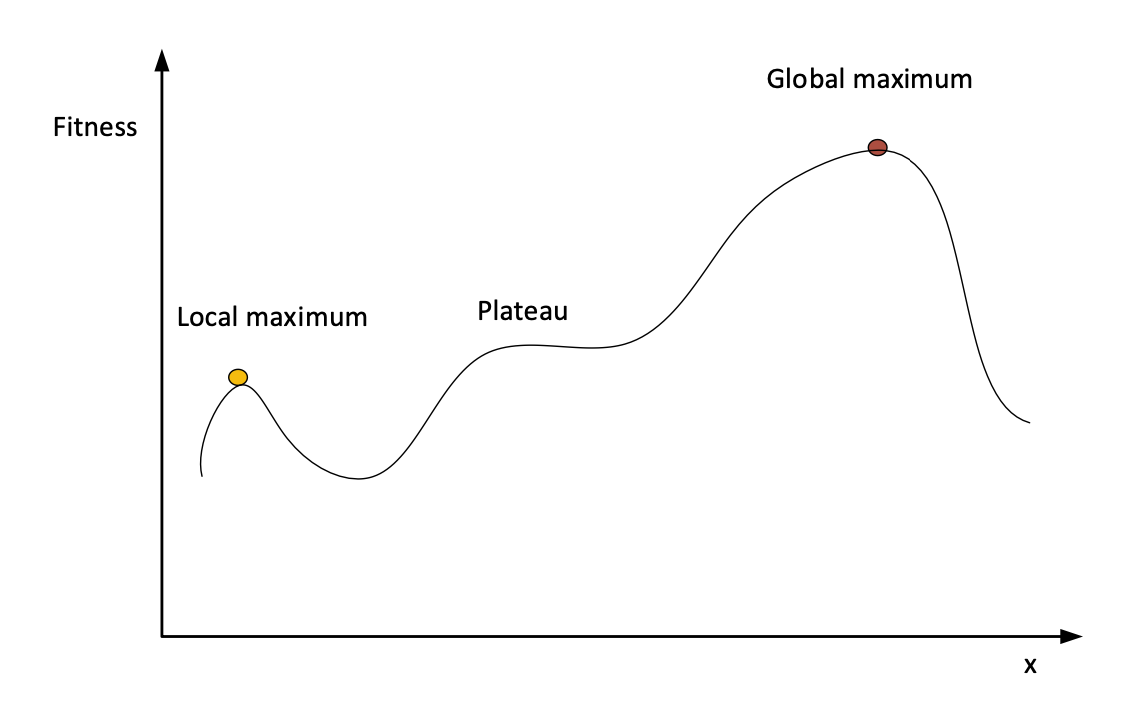
Randomised search vs Local search 隨機搜索 vs 局部搜索
- Randomised search: 隨機搜索:
- Good at exploration, e.g., to search large unknown region of the search space 善於探索,例如搜索搜索空間的大未知區域
- Not good at exploitation, e.g., to search small region around the current solution 善於開發,例如搜索當前解決方案附近的小區域
- Especially bad for problems where good solutions are just a small portion of all possible solutions 尤其不適合好的解決方案只是所有可能解決方案的一小部分的問題
- Local search: 局部搜索:
- Good at exploitation: capable to find local optimum 善於開發:能夠找到局部最優解
- Not good at exploration: gets stuck into local optimum 很難探索:陷入局部最優解
- Question: how to find global optimum? 問題:如何找到全局最優解?
Stochastic local search: Main idea 隨機局部搜索:主要思想
- Main idea: escape or avoid local optima 主要思想:逃脫或避免局部最優解
- How: Introduce randomness into local search algorithm to escape from local optima 如何:將隨機性引入局部搜索算法以逃脫局部最優解
- Escape strategies: 逃脫策略:
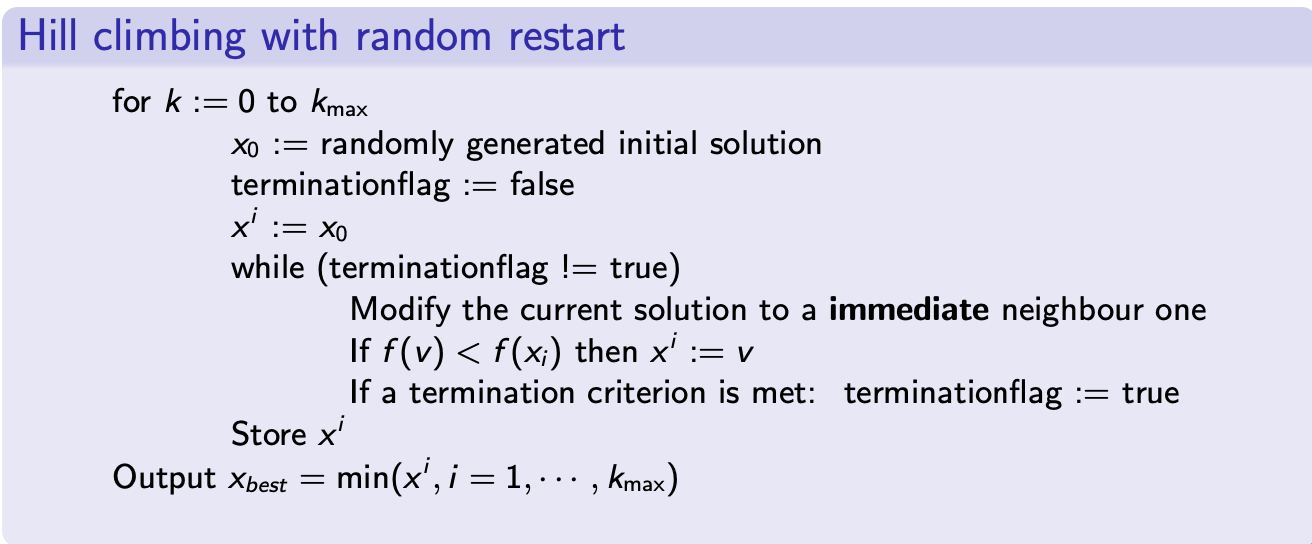
- Random restart: simply restart the local search from a random initial solution 簡單地從隨機初始解重新啟動局部搜索
- Applicable when: 適用於:
- Number of local optima is small 本地最優解的數量很小
- The cost for restarting the local search is cheap 重新啟動局部搜索的成本很低
- Applicable when: 適用於:
- Perform random non-improving step: randomly move to a less fit neighbour – Simulated Annealing 執行隨機非改進步驟:隨機移動到不太適合的鄰居——模擬退火
- Random restart: simply restart the local search from a random initial solution 簡單地從隨機初始解重新啟動局部搜索
Hill climbing with random restart 爬山演算法加上隨機重啟
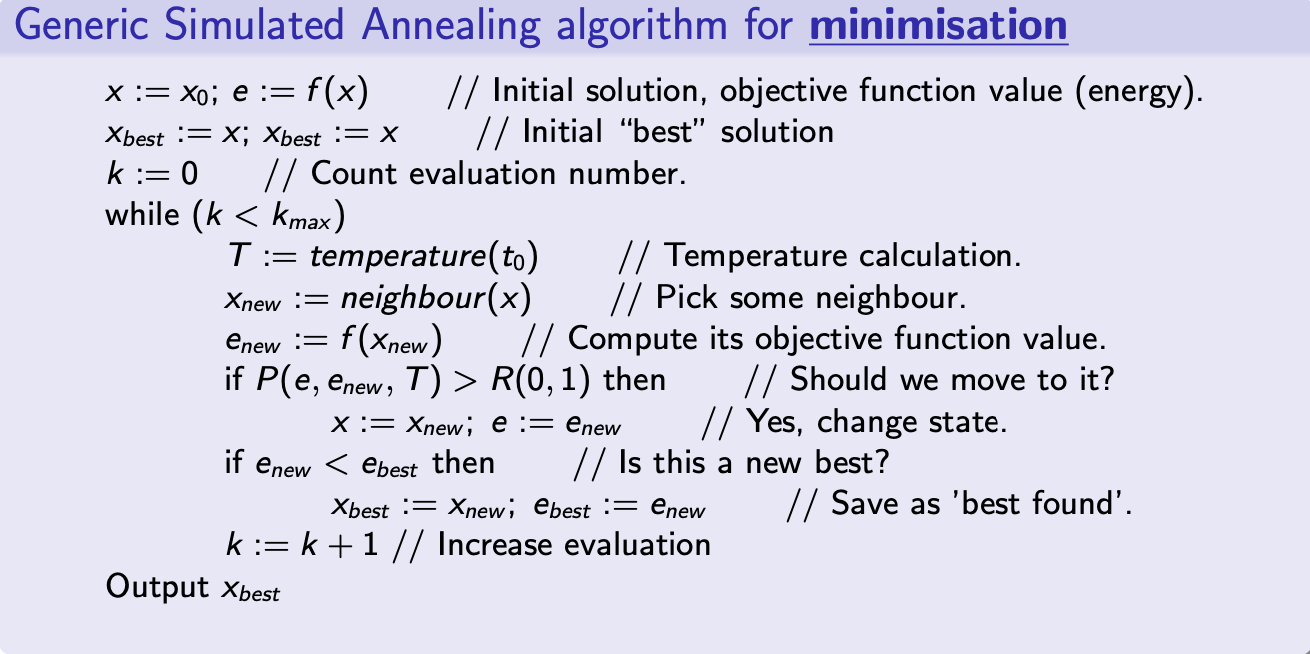
Simulated Annealing 模擬退火
- Simulated Annealing: a generic heuristic algorithm for optimisation problems proposed by Kirkpatrick in 1983 [1]. 模擬退火:由 Kirkpatrick 在 1983 年提出的一種通用的用於優化問題的啟發式算法 [1]。
- Inspired by annealing in metallurgy: 靈感來自冶金中的退火:
- "heat treatment that alters a material to increase its ductility and to make it more workable" "改變材料以增加其延展性並使其更易加工的熱處理"
- The real annealing: 真正的退火:
- Step 1: heating a material to above its critical temperature 使材料加熱到其臨界溫度以上
- Step 2: maintaining a suitable temperature for a period of time 維持適當的溫度一段時間
- Step 3: cooling the material to below its critical temperature 使材料冷卻到其臨界溫度以下
- In annealing: find a state of lower thermodynamic free energy for metal 熱處理:為金屬找到較低熱力學自由能的狀態
- In optimisation: find a solution to get to the minimum of an objective function 優化:找到一個解決方案以達到目標函數的最小值
if and otherwise
Annealing schedule temperature() defines how to decreased temperature from an initial temperature . 退火計劃 temperature() 定義如何從初始溫度 降低溫度。
- Without the analogue from metallurgy, SA algorithm is essentially a stochastic local search algorithm 如果沒有冶金類比,SA 算法本質上是一種隨機局部搜索算法
- Main idea: Escape from local optima with random non-improving step: 避免局部最優解的主要思想:
- Accepting better solutions with the probability of 1, e.g., P := 1 if enew < e, i.e., enew is better than e
- Accepting worse solutions with a certain probability, e.g., if , i.e., enew is worse than e
- This allows SA to explore more of the possible search space of solutions. 這允許 SA 探索更多可能的解決方案搜索空間。
- T, which is determined by the annealing schedule
temperature(), will decrease, so the probability of accepting worse solutions will decrease. T 由退火計劃temperature()確定,將減少,因此接受較差解決方案的概率將減少。 - Question: what happen if
temperature()reaches 0? 問題:如果 temperature() 到達 0 呢?
Search trajectory of simulated annealing 模擬退火的搜索軌跡
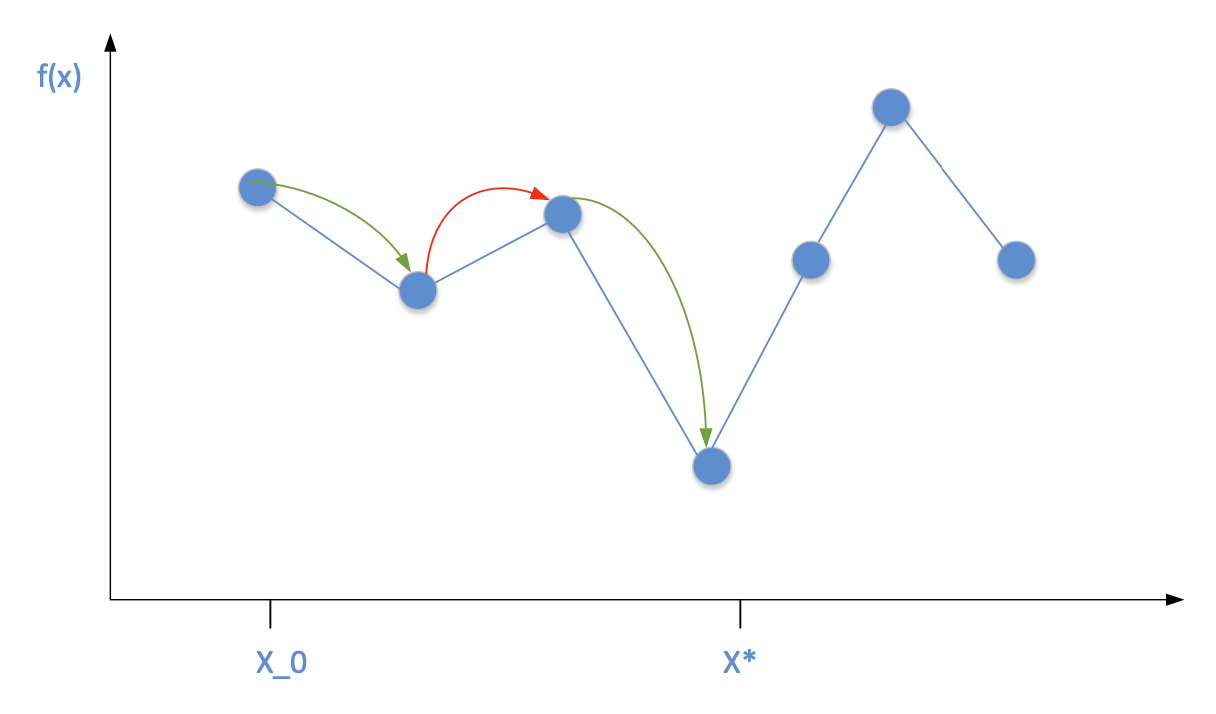
Wait!
- Main idea: escape or avoid local optima 主要思想:逃脫或避免局部最優解
- Algorithm uses the 'avoiding' strategy: Tabu search 算法使用"避免"策略:禁忌搜索
Conclusion 結論
- Local search algorithms is simple but can generate good solutions for many problems 本地搜索算法簡單,但可以為許多問題生成良好的解決方案
- However, local search algorithms only focus on exploitation, which will lead to local optima 但是,局部搜索算法僅關注利用,這將導致局部最優解
- Different stochastic local search algorithms use different strategies to escape or avoid local optima 不同的隨機局部搜索算法使用不同的策略來逃脫或避免局部最優解
- Stochastic local search algorithms usually produce better results using default parameters than local search algorithms 通常使用默認參數的隨機局部搜索算法會產生比局部搜索算法更好的結果
- However, tuning stochastic local search algorithms to get better results is difficult, it is an art! 然而,調整隨機局部搜索算法以獲得更好的結果是困難的,這是一門藝術!
Reading list
- Solving the Large-Scale TSP Problem in 1 h: Santa Claus Challenge 2020
- See how acellular slime mold solve TSP Remarkable problem-solving ability of unicellular amoeboid organism and its mechanism
[1]: G.A. Croes. A method for solving traveling-salesman problems. Operations Research. 1958