Image Segmentation 圖像分割
Digital images 數碼影像
- Image representations 圖像表示
- 2dimensional arrays of pixels 二維像素陣列
- multi-dimensional arrays of pixels 多維像素陣列
- (x,y,z)
- (x,y,t)
- (x,y,z,t)
- (x,y,z,b 1 ,b 2 , ... , bN)
Characterising images as objects 圖像物件特徵
- Spatial resolution 空間解析度
- Pixel size 像素大小
- Pixels / inch 像素/英吋
- Intensity resolution 亮度解析度
- Time resolution 時間解析度
- Spectral resolution 色彩解析度
- Number of bands 波段數 + bandwidth 帶寬
Characterising images as signals 圖像信號特徵
- Image statistics 圖像統計
- Mean, standard deviation 平均值、標準差
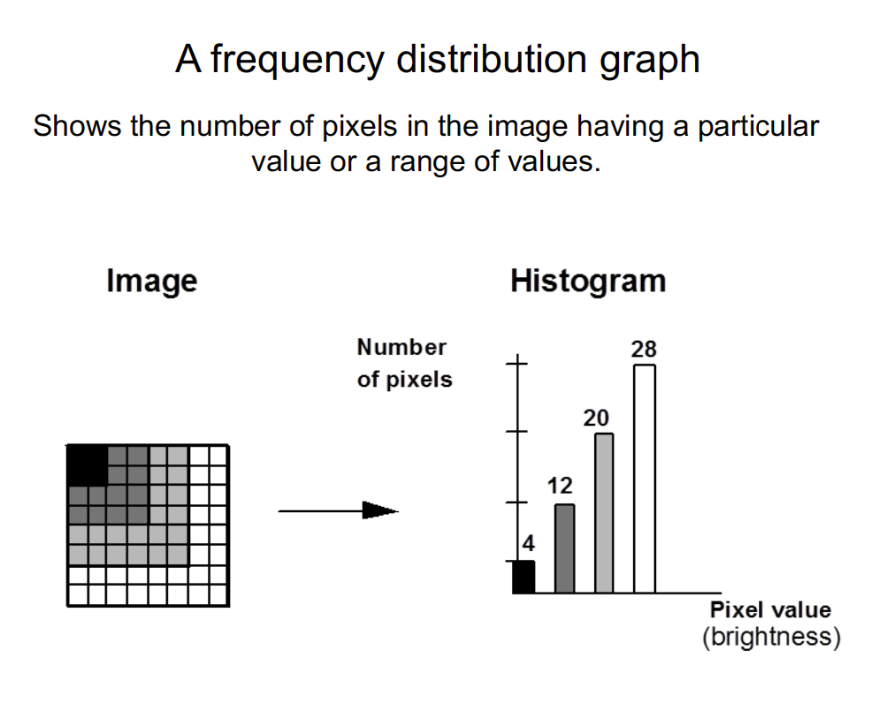
- Histogram: frequency distribution graph 直方圖:頻率分佈圖
Characterising images as signals 圖像信號特徵
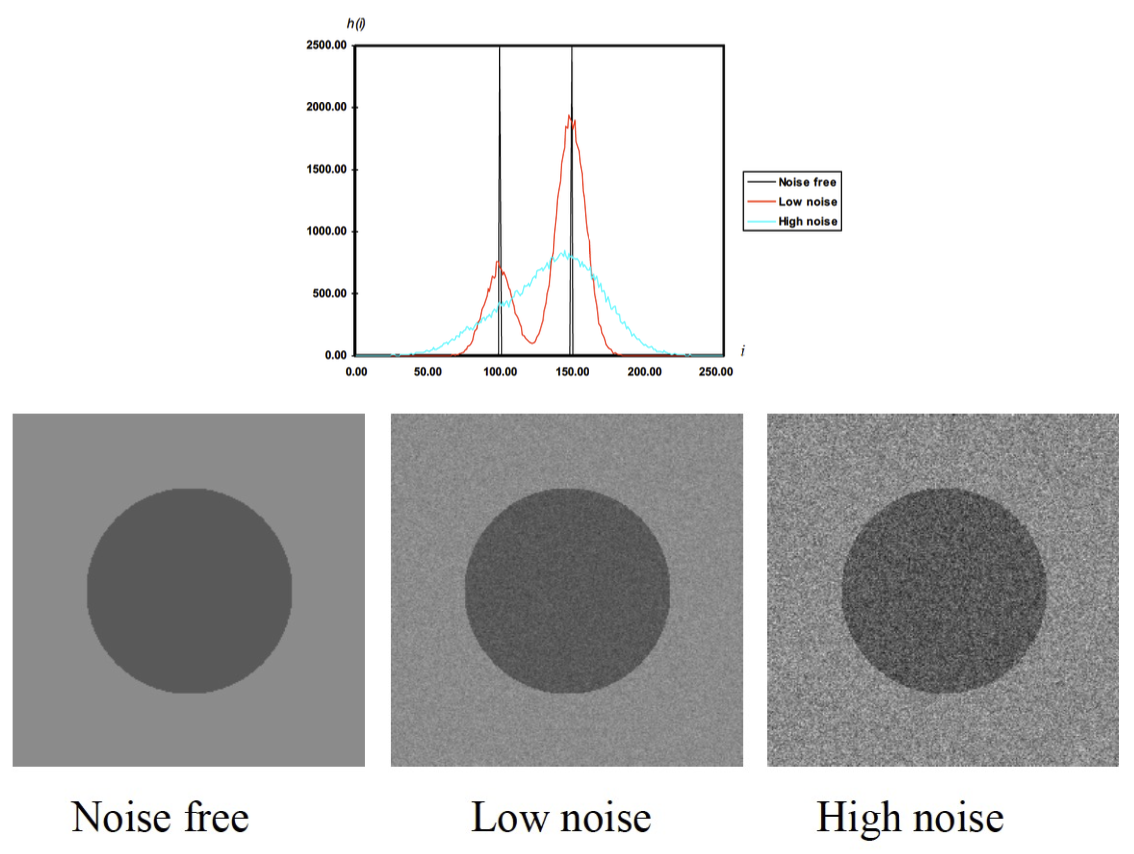
- Image noise 圖像雜訊
- Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) 信號雜訊比
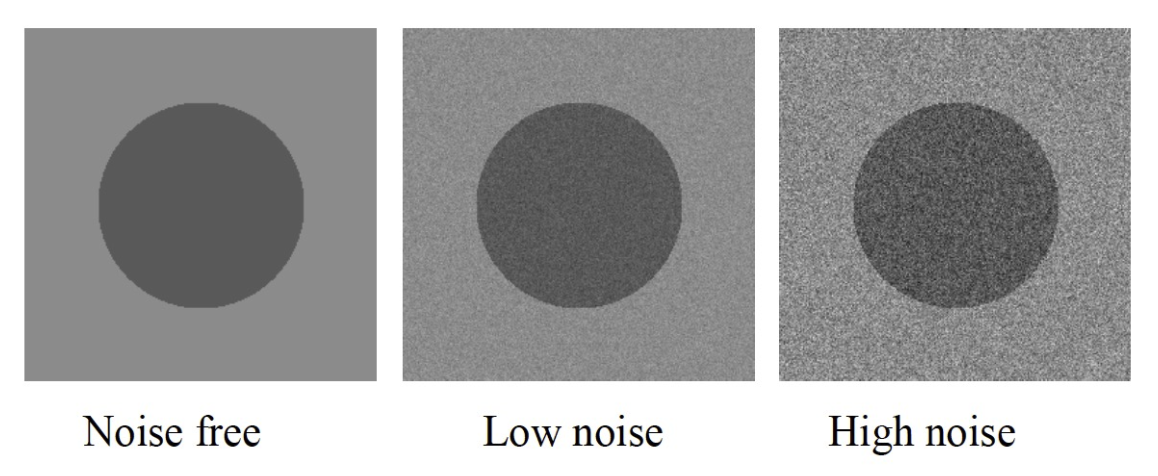

Characterising images as objects 圖像物件特徵
- This requires that image is partitioned into meaningful regions. 這需要將圖像劃分為有意義的區域。
- The process of partitioning is known as segmentation 分割的過程稱為分割。
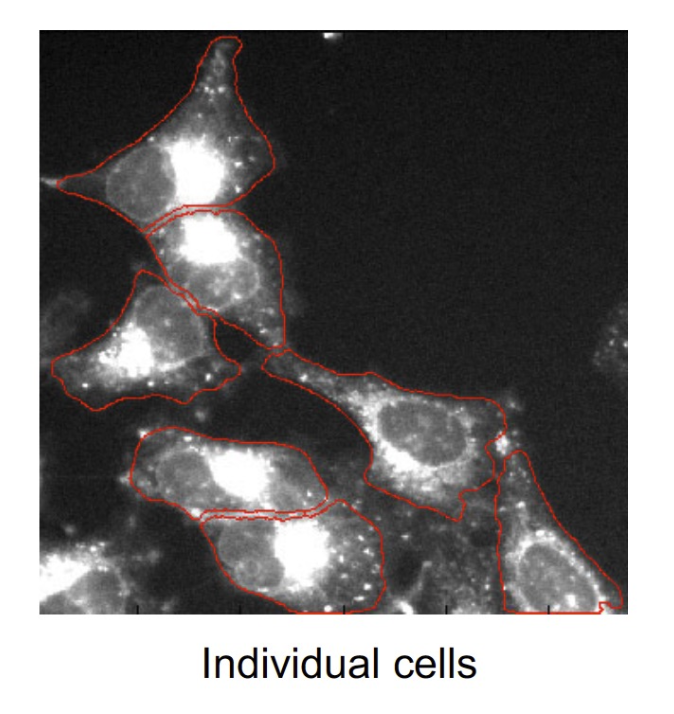
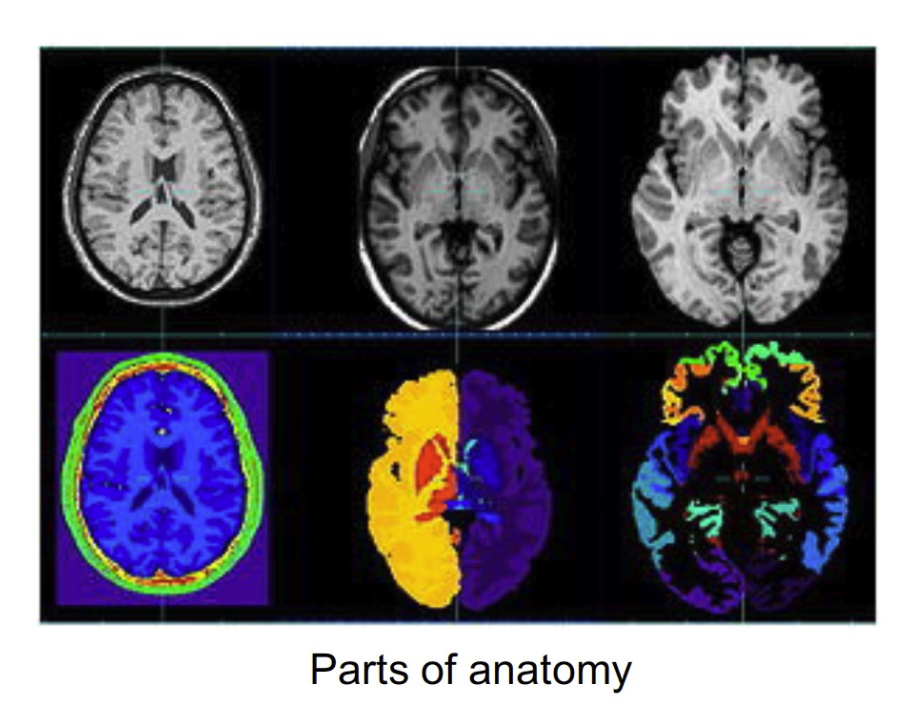
Image Segmentation 圖像分割
- Partitioning an image into meaningful regions with respect to a particular application 針對特定應用程序將圖像劃分為有意義的區域
- Simple segmentation is based on measurements taken from the image and might be based on brightness (grey-level), colour, texture, motion, etc. 簡單的分割是基於從圖像中取得的測量值,可能基於亮度(灰階),顏色,紋理,運動等。
Image segmentation techniques 圖像分割技術
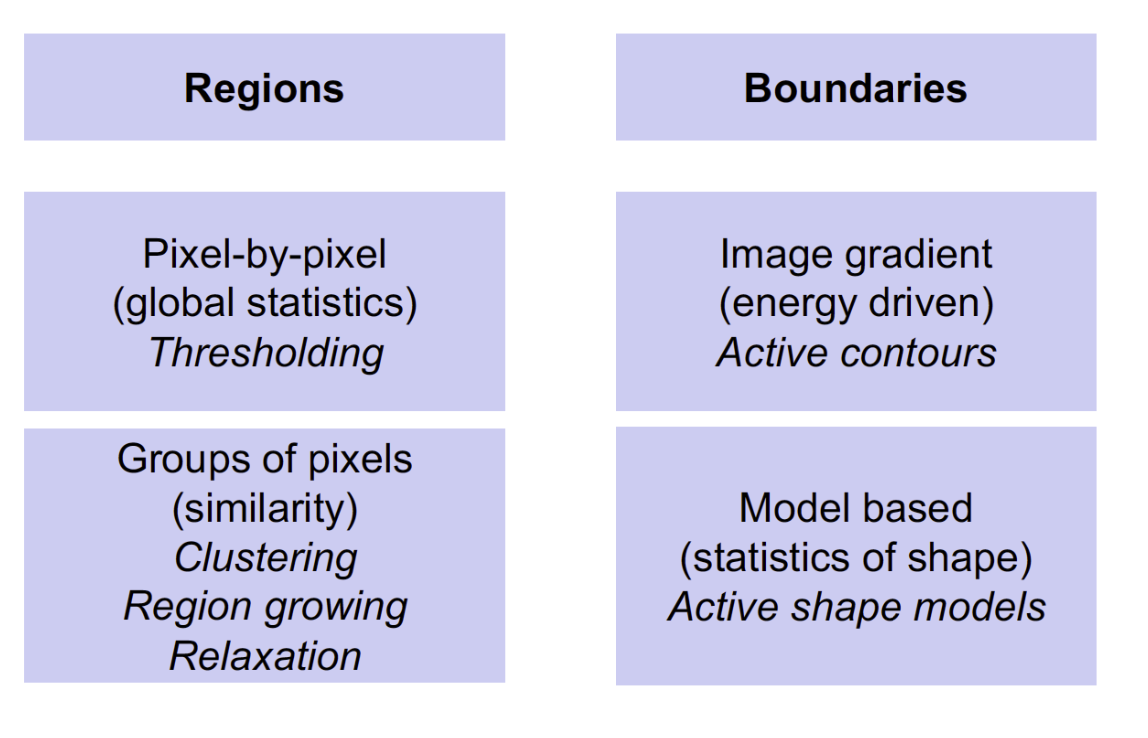
Image Segmentation 圖像分割
- Image Segmentation can be classified as: 圖像分割可以分類為:
- Non-automated 非自動化
- Identifying regions by hand! 手動識別區域!
- Semi-automated 半自動化
- Thresholding 閾值
- Region Growing 區域生長
- Active Contour, etc ... 主動輪廓等...
- Automated 自動化
- Model based segmentation 基於模型的分割
- Area of intensive research 高度研究
Non-automated segmentation 非自動化分割
- Given an image, select and define a region of interest by hand. 給定一個圖像,手動選擇和定義感興趣的區域。
- Rough estimate of the region of interest. 感興趣區域的粗略估計。
Hand Segmentation? 手動分割?
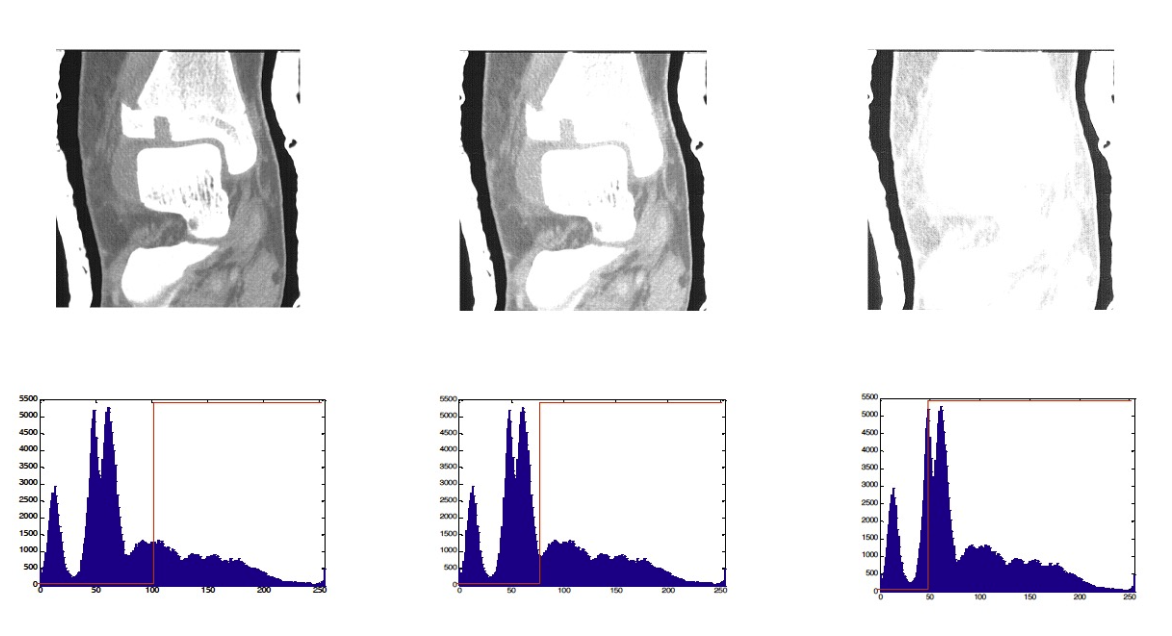
Thresholding 閾值
- Histogram-based segmentation (thresholding) 基於直方圖的分割(閾值)
- Given an image, select a suitable threshold value to separate the image into two regions. 給定一個圖像,選擇一個適當的閾值來將圖像分割為兩個區域。
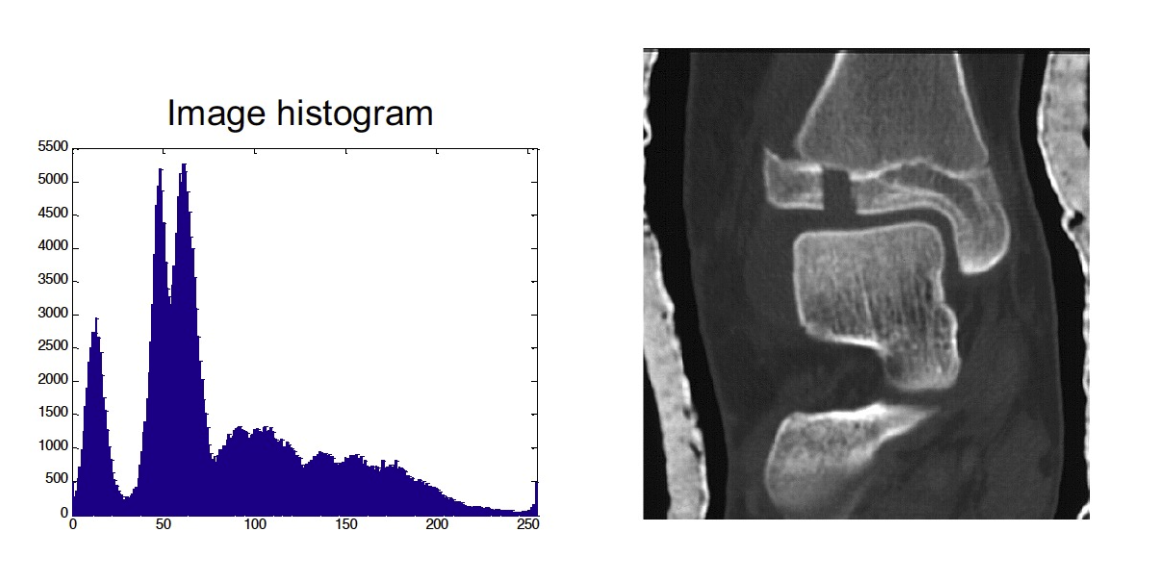
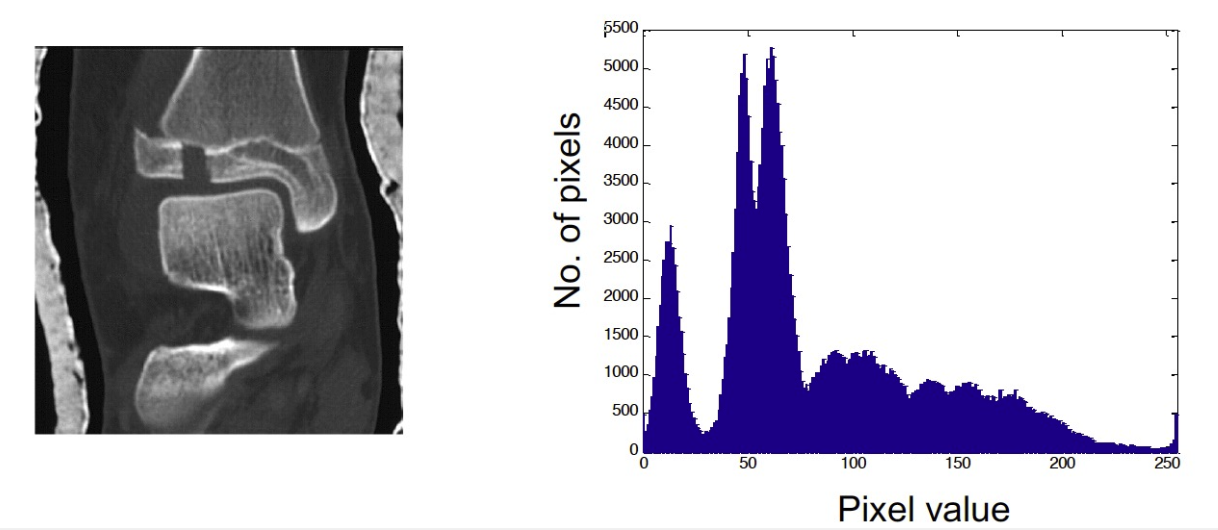
Histogram of an image 圖像的直方圖
Thresholding 閾值
Thresholding challenges 閾值挑戰
Thresholding challenges 閾值挑戰
Thresholding challenges 閾值挑戰
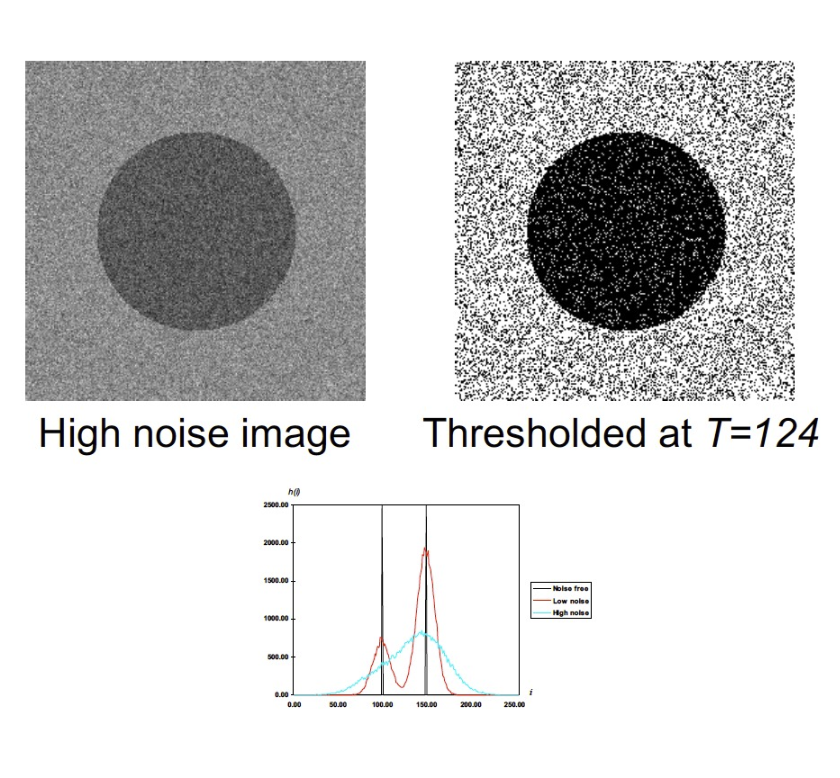
Thresholding challenges 閾值挑戰
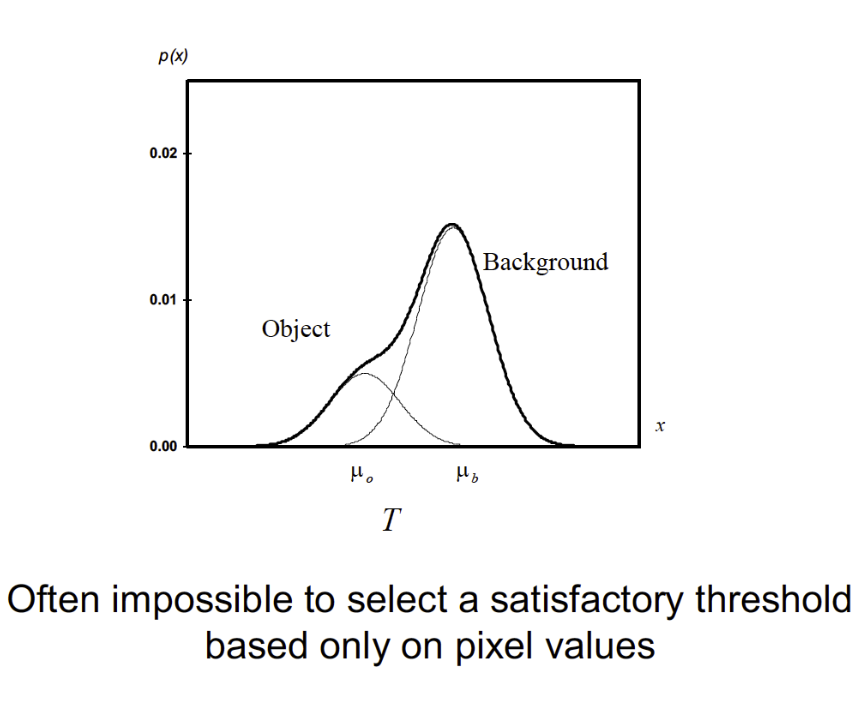
Thresholding challenges 閾值挑戰
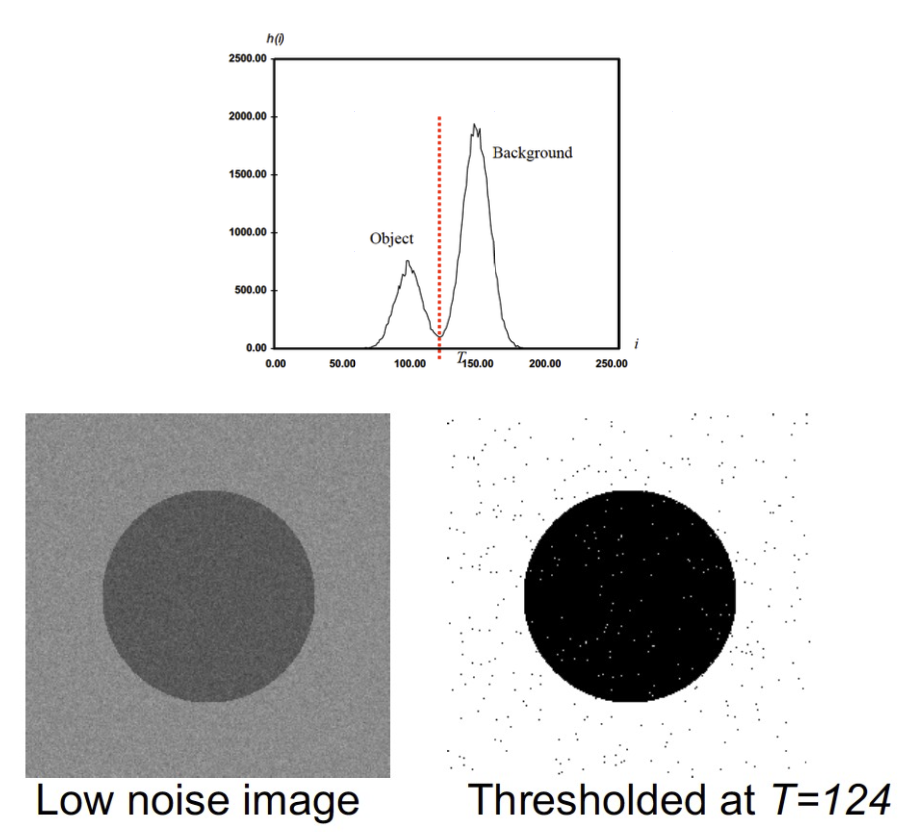
- How do we determine the threshold? 我們如何確定閾值?
- Many approaches possible 可能有很多方法
- Interactive threshold 互動門檻
- Adaptive threshold 自適應閾值
- Variance minimisation method (Otsu's threshold selection algorithm) 方差最小化法(大津的閾值選擇算法)
- In the simplest form, the algorithm returns a single intensity threshold that separate pixels into two classes, foreground and background. 在最簡單的形式中,該算法返回一個強度閾值,將像素分為兩個類別,前景和背景。
- This threshold is determined by minimizing intra-class intensity variance, or equivalently, by maximizing inter-class variance. 這個閾值是通過最小化類內強度變異數來確定的,或者通過最大化類間變異數來確定。
Otsu's Threshold Selection Algorithm 大津的閾值選擇算法

Thresholding - Problems 閾值 - 問題
- Manual methods:
- Time consuming
- Operator error
- Subjective
- Different regions / image areas may need different levels of threshold 不同的區域/圖像區域可能需要不同的閾值水平
- Noise
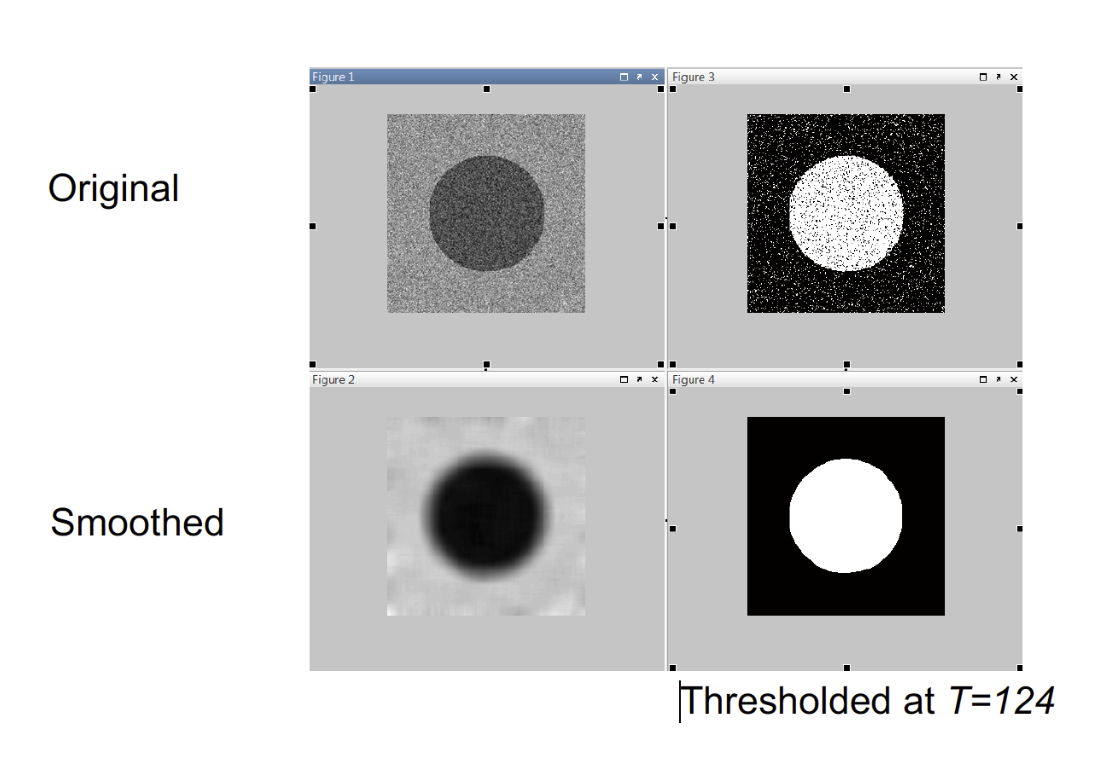
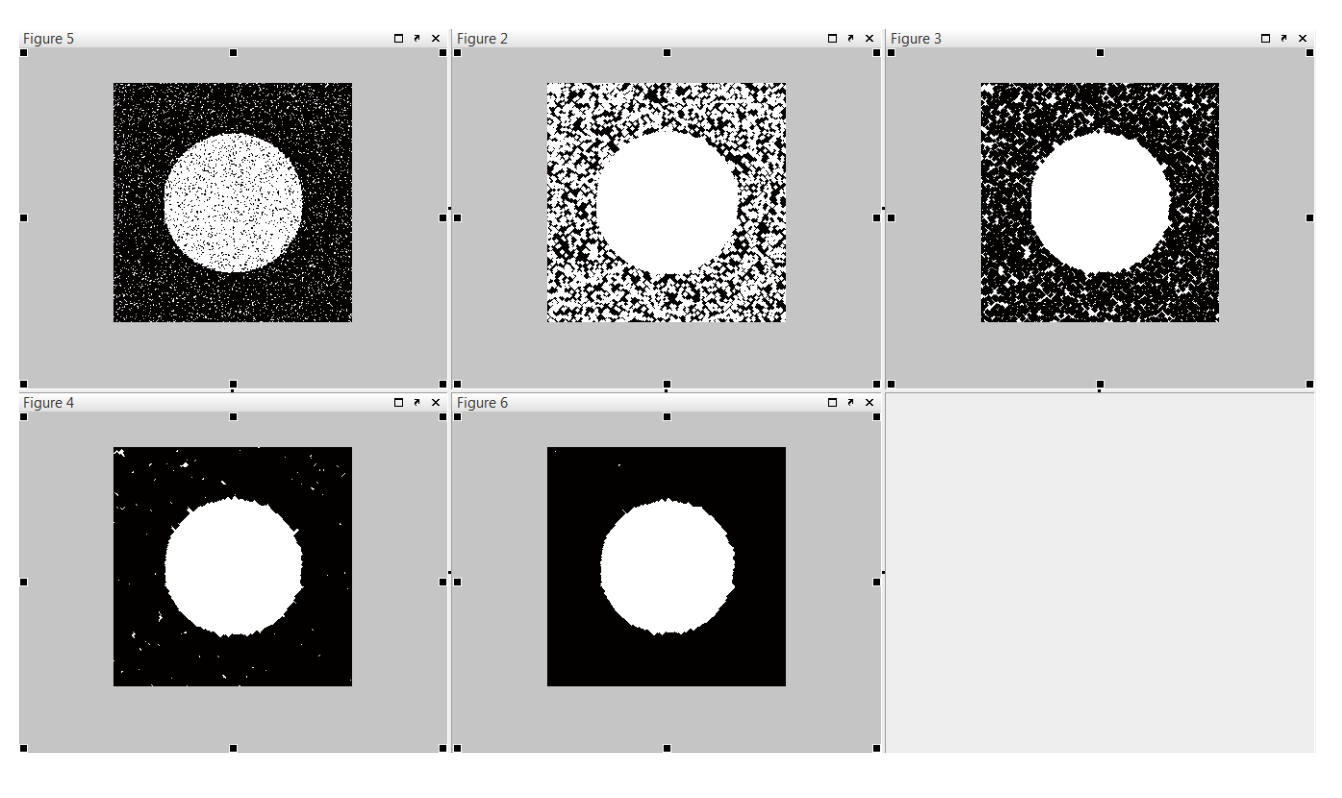
Smoothing & Thresholding 平滑和閾值
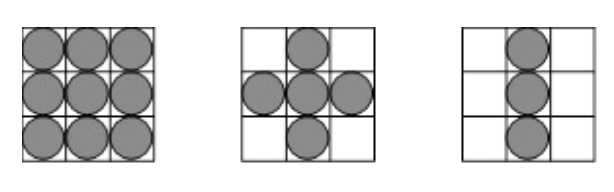
Mathematical morphology 數學形態學
- Morphology is concerned with study of form and shape. 形態學關注形式和形狀的研究。
- Operations of mathematical morphology are defined in terms of interactions of two sets of points. One set (usually a large one) corresponds to an image; the other (usually much smaller) is called a structuring element. 數學形態學的操作是根據兩組點的互動來定義的。一組(通常是一個大的)對應於一個圖像;另一組(通常要小得多)稱為結構元素。
- A structuring element can be thought of as a "brush" with which an image is "overpainted" in a number of specific ways, depending on the morphological operation. 結構元素可以被認為是一個"筆刷",用於以多種特定方式"重新繪製"圖像,具體取決於形態學操作。
- Examples of typical structuring elements (grey dots indicate "active" members of the structuring element set): 結構元素的典型示例(灰色點表示結構元素集的"活動"成員):
Mathematical morphology 數學形態學
- Two principal operations of mathematical morphology are dilation and erosion. 數學形態學的兩個主要操作是膨脹和侵蝕。
- Dilation (expansion) 膨脹(擴展)
- adding a "layer" of pixels to the periphery of objects 在對象的外圍添加一個像素"層"
- the object will grow larger, close objects will be merged, holes will be closed 這個對象將變大,接近的對象將被合併,洞將被關閉
- Erosion (shrinking) 侵蝕(縮小)
- removing a "layer" of pixels all round an object 一個對象周圍移除一個像素"層"
- the object will get thinner, if it is already thin it will break into several sections 這個對象將變得更薄,如果它已經很薄,它將分成幾個部分
Mathematical morphology 數學形態學
Advanced segmentation methods 進階分割方法
- Active contours (snakes) 活動輪廓(蛇)
- Watershed segmentation 水域分割
- Level-set methods 等級集方法
- Active shape model segmentation 活動形狀模型分割
Active (snake) contours 活動(蛇)輪廓
E[(C)(p)]=α∫01Eint (C(p))dp+β∫01Eimg(C(p))dp+γ∫01Econ (C(p))dp
- The internal term stands for regularity/smoothness along the curve and has two components (resisting to stretching and bending) 輪廓內部項代表沿輪廓的規則性/平滑性,並具有兩個部分(抵抗拉伸和彎曲)
- sensitivity to the amount of stretch in the snake and the amount of curvature in the snake 對蛇的拉伸量和蛇的曲率量的敏感性
- The image term guides the active contour towards the desired image properties (strong gradients) 圖像項引導活動輪廓向所需的圖像屬性(強梯度)靠近
- Energy in the image is some function of the features of the image, for example edges 圖像中的能量是圖像特徵的某種函數,例如邊緣
- The external term can be used to account for use defined constraints, or prior knowledge on the structure to be recovered 外部項可用於考慮用戶定義的限制,或對要恢復的結構的先驗知識
- allowes for user interaction to guide the snakes, not only in initial placement but also in their energy terms. 使用戶交互來引導蛇,不僅在初始放置中,而且在它們的能量項中。
- The lowest potential of such a cost function refers to an equilibrium of these terms 最低潛力的成本函數指的是這些項的平衡
Active contours 活動輪廓
E[(C)(p)]=α∫01Eint (C(p))dp+β∫01Eimg(C(p))dp+γ∫01Econ (C(p))dp
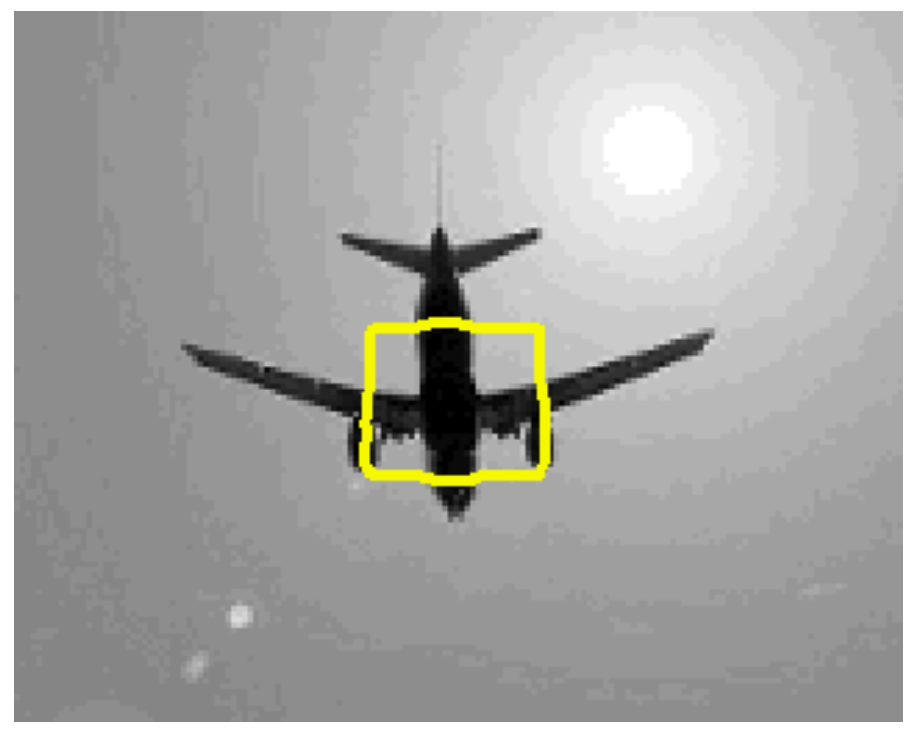

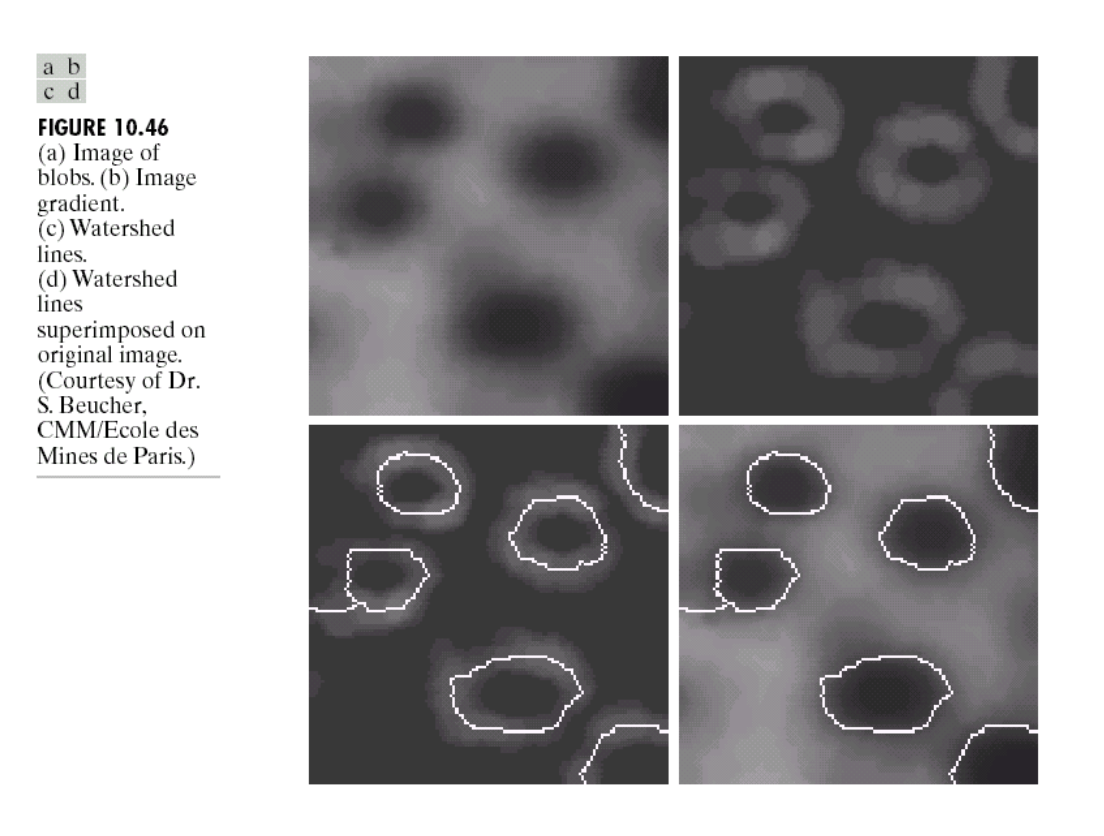
Watershed segmentation 水域分割
- Classify pixels into three classes: 分類像素為三類:
- belonging to a local minimum 屬於局部最小值
- catchment basin or watershed: pixels at which a drop of water would flow to that local minimum 捕捉盆地或水域:像素,水滴將流向該局部最小值
- divide of watershed lines: pixels at which water would flow to two minima. 水域線的分割:像素,水將流向兩個最小值。
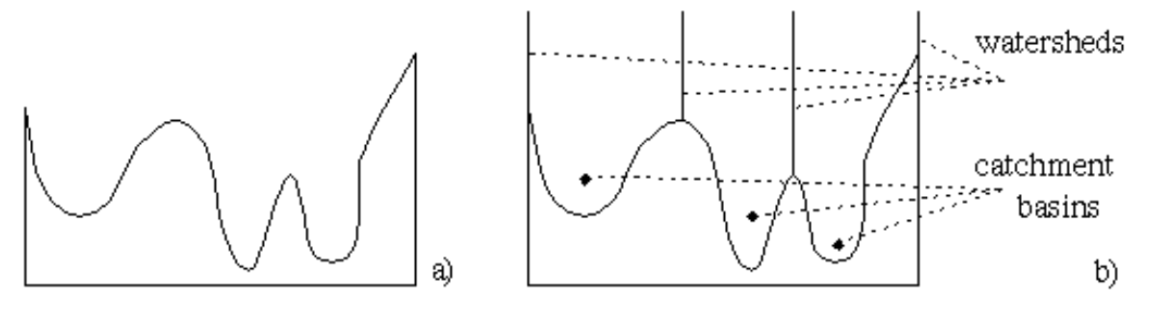
Watershed segmentation 水域分割