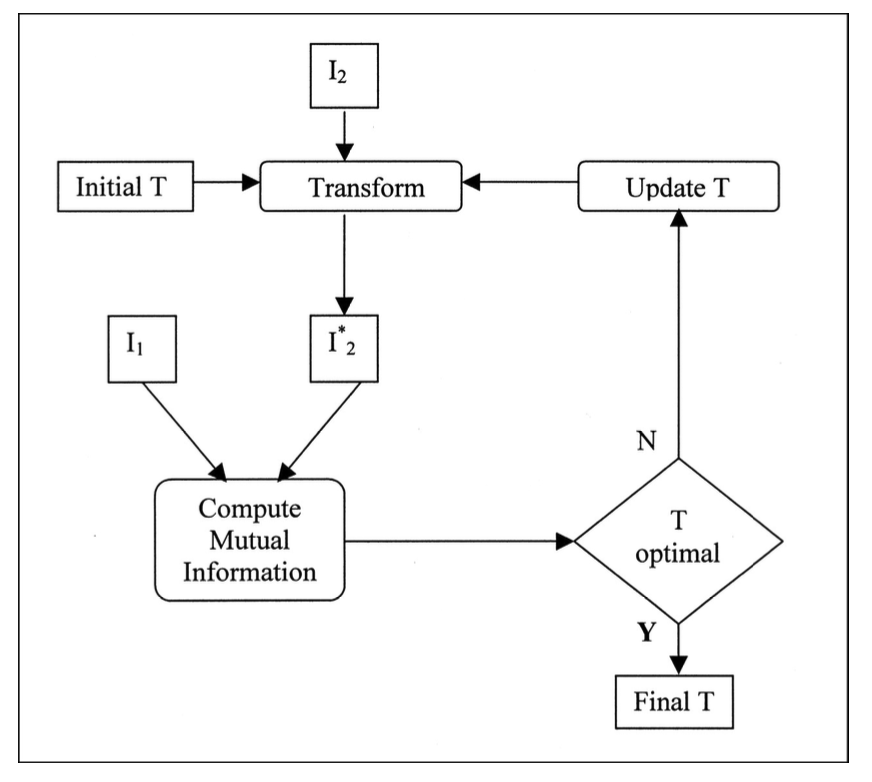
Image Registration 圖像配準
A Probabilistic Atlas of the Human Brain in Alzheimer's Disease: Emerging Patterns of Variability, Asymmetry and Degeneration 阿爾茨海默病中人腦的概率圖譜:變異性、不對稱性和退化的新模式
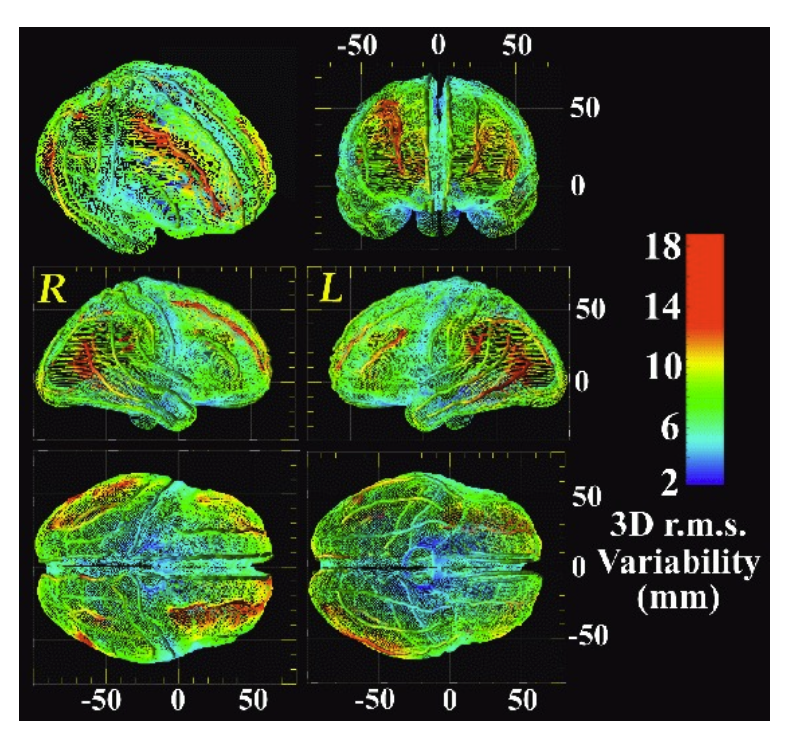
Image registration 圖像配準
- Geometric (and Photometric ) alignment of one image with another 幾何(和光度)一幅圖像與另一幅圖像的對齊
- Implemented as the process of estimating an optimal transformation between two images. 作為估計兩幅圖像之間最佳變換的過程
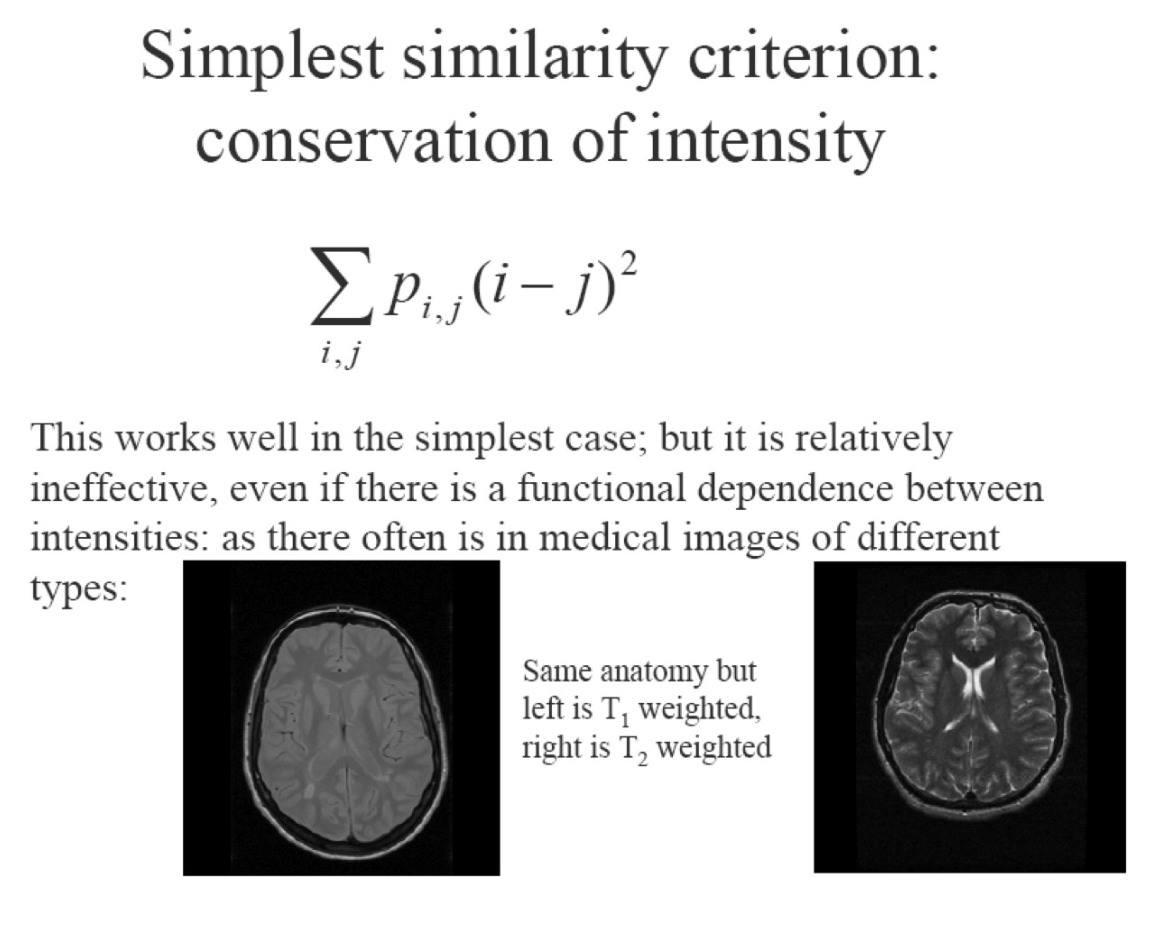
- Images may be of same or different types (MR, CT, visible, fluorescence, ...) 圖像可能是相同或不同類型的(MR,CT,可見,荧光,...)
Image registration 圖像配準
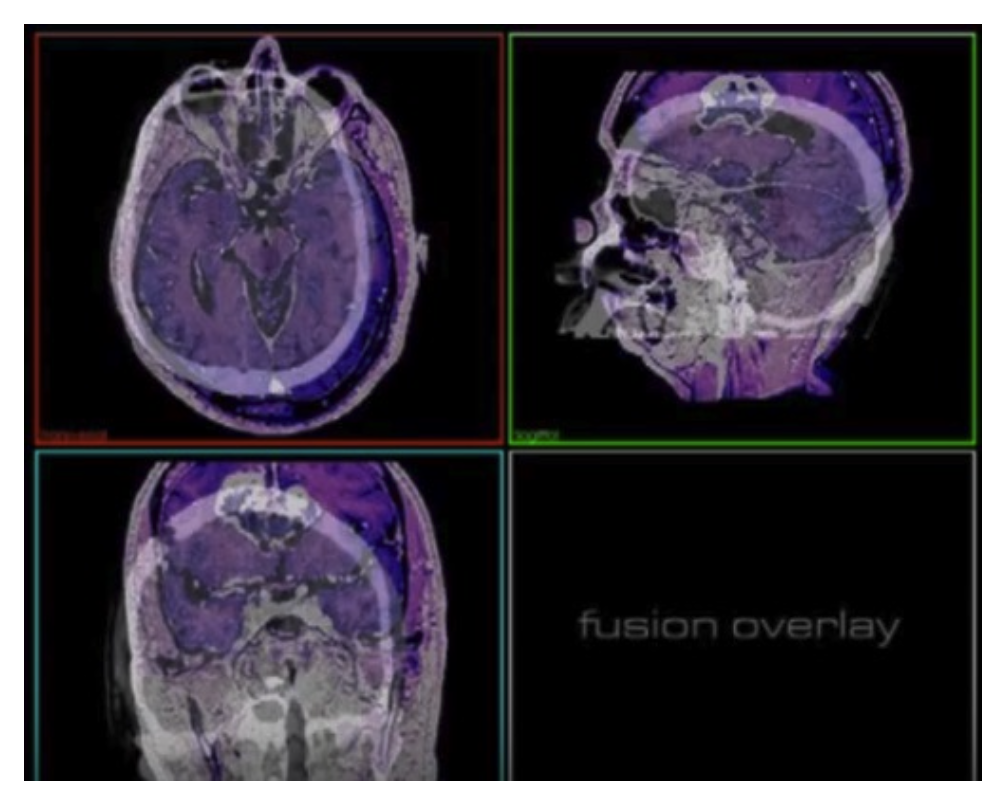
Examples of image registration 圖像配準的例子
- Individual 個人
- Aligning an image taken now with one taken on a previous occasion (monitor the progression of disease, discover the fact of a disease) 現在與以前拍攝的圖像對齊(監控疾病的進展,發現疾病的事實)
- Aligning two images of different sorts (e.g. MRI and CT) of the same patient (data fusion) 將兩幅不同類型的圖像(例如 MRI 和 CT)對齊同一個病人的圖像(數據融合)
- Groups 團體
- Aligning the images of patients and aligning those of normals to develop a statistical model of variation associated with a disease; e.g. Alzheimer's disease 配準病人的圖像,並將正常人的圖像對齊,以開發與疾病相關的變異的統計模型,例如阿爾茨海默病
- Aligning the images from many thousands of subjects around the world as part of a clinical/drug trial 將世界各地數千名受試者的圖像對齊作為臨床/藥物試驗的一部分
Components of registration 配準的組件
- The registration problem can be formulated as: 配準問題可以被公式化為:

- Find transformation T (defined by a parameter vector p ) that minimises the difference between the reference image I and target image J (defined by a parameter vector q ) 找到變換 T(由參數向量 p 定義)使參考圖像 I 和目標圖像 J(由參數向量 q 定義)之間的差異最小化
Components of registration 配準的組件
- Issues to consider 需要考慮的問題
- What entities do we match? Features, intensities, ... 我們匹配哪些實體?特徵,強度,...
- What class of transforms? Rigid, affine, spline warps, ... 什麼類別的轉換?剛性,仿射,樣條扭曲,...
- What similarity criterion to use? Normalised cross-correlation, ... 使用什麼相似性標準?歸一化互相關,...
- What search algorithm to find the minimum T? 找到最小 T 的搜索算法是什麼?
- What interpolation method to use? Bilinear, spline, ... 使用什麼插值方法?雙線性,樣條,...
Reference and target datasets 參考和目標數據集
- Landmarks / control points 地標/管制站
- Image values 圖像值
- Feature images (e.g. edge images) 特徵圖像(例如邊緣圖像)
- Combinations of the above 以上組合
Landmarks 地標
Landmark Matching 地標匹配
Other features 其他特徵
- Image values (intensities) 圖像值(強度)
- Edges, contours or surfaces 邊緣,輪廓或表面
- Salient features 顯著特徵
- Corners 角落
- Centres 中心
- Points of high curvature 高曲率點
- Line intersections 線交點
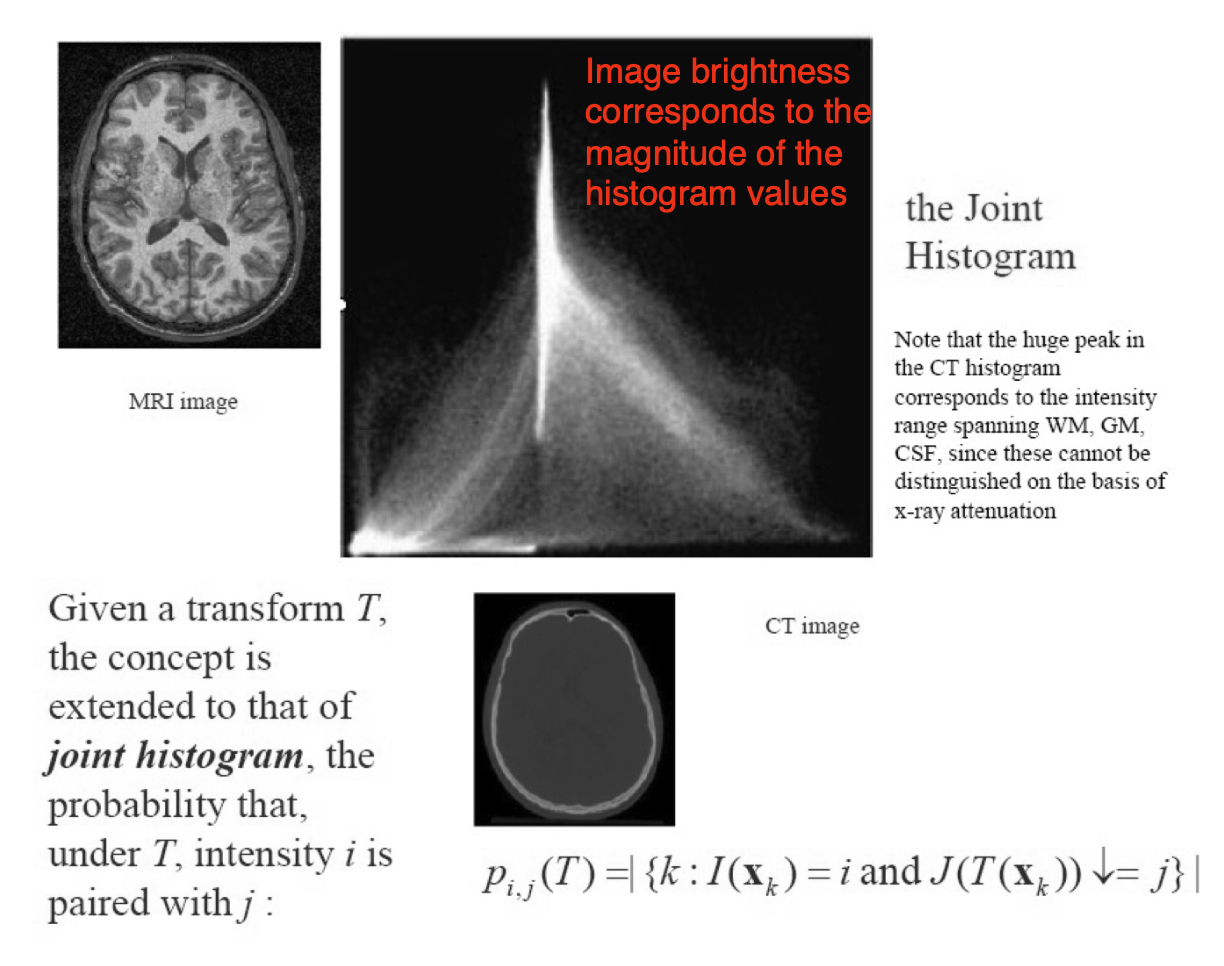
Joint histogram 聯合直方圖
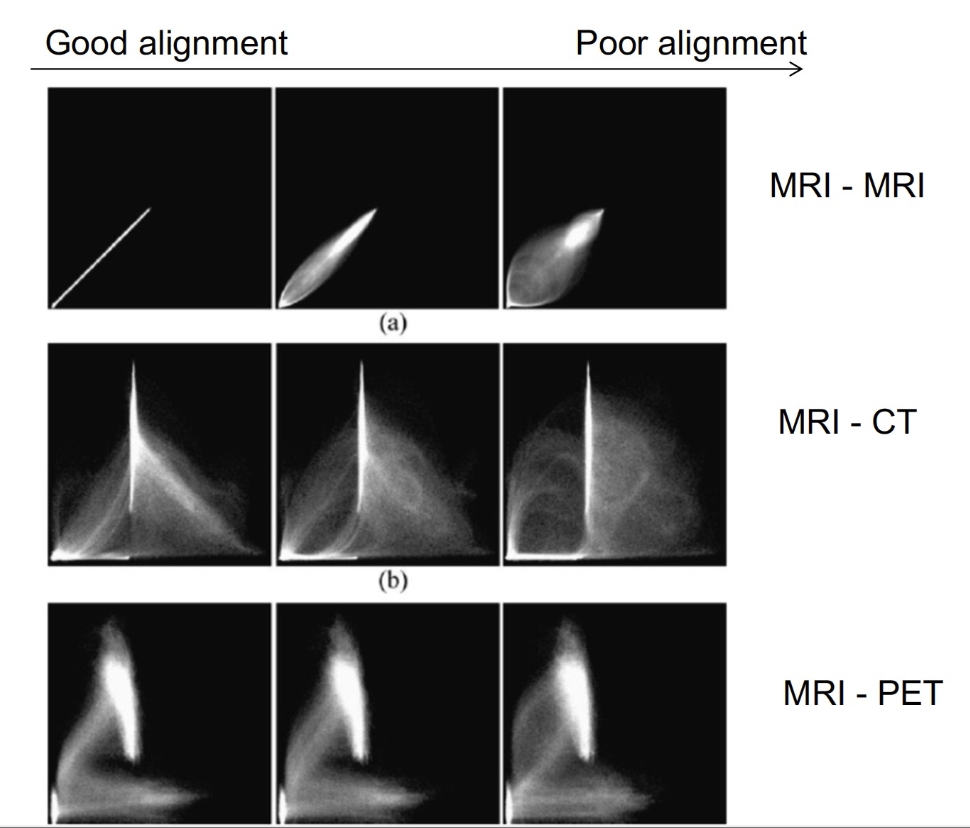
- Heuristic observation is that when images are 啟發式觀察是,當圖像是
- well aligned, the joint histogram appears "sharpest" 對齊良好,聯合直方圖顯得"最銳利"
Transformation Model 轉換模型
- Rigid 死板的
- Affine 仿射的
- Piecewise affine 分段仿射的
- Non-rigid or elastic 非剛性或彈性
Rigid Transformation Model 剛性轉換模型
- Used for within-subject registration when there is no distortion 用於無失真時的主體內配準
- Composed of 3 rotations and 3 translations 由 3 個旋轉和 3 個平移組成
- Linear – can be represented as a 4x4 matrix 線性——可以表示為 4x4 矩陣
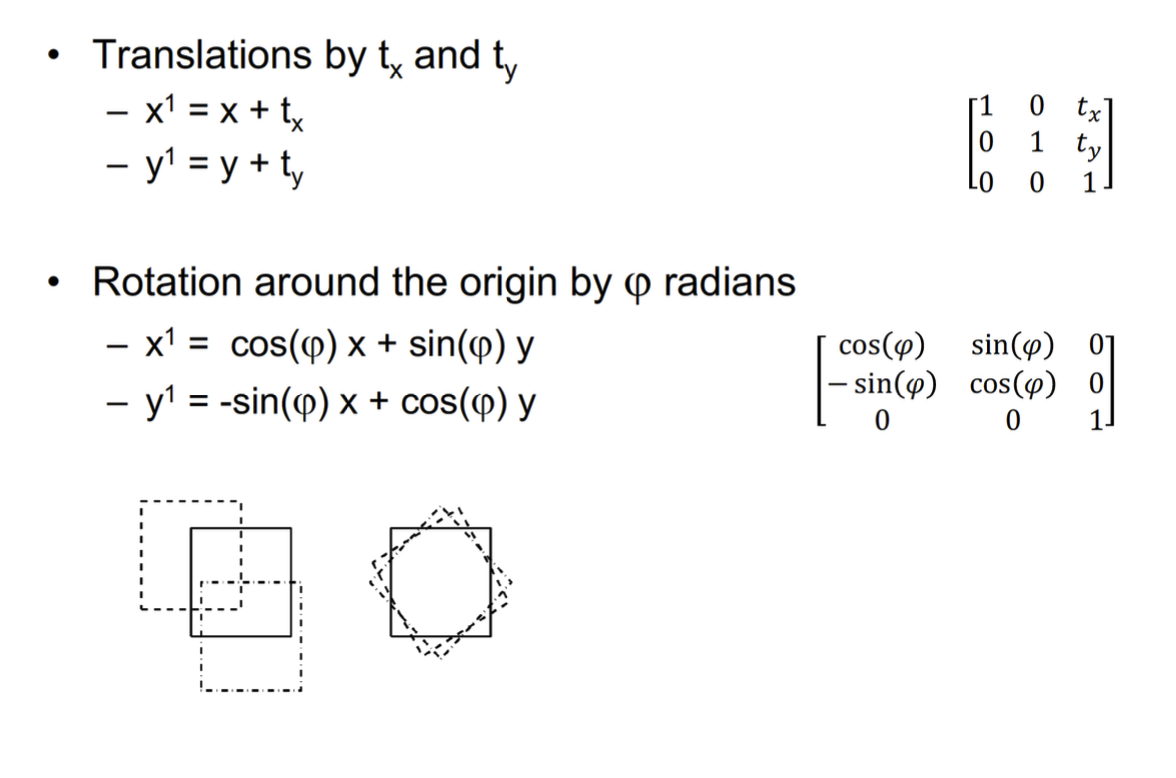
2D Rigid Transforms 2D 剛性轉換
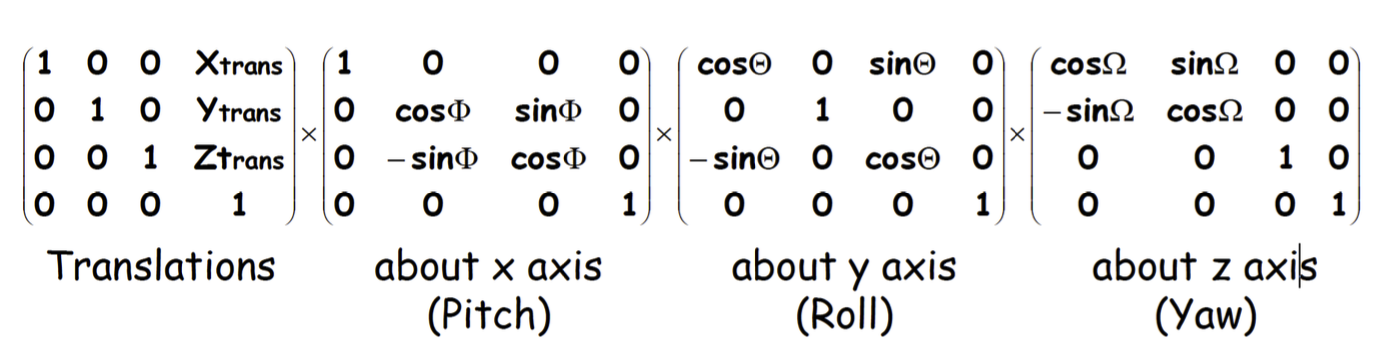
3D Rigid-body Transformations 3D 剛性體轉換
- A 3D rigid body transform is defined by: 3D 剛性體轉換由以下定義:
- 3 translations - in X, Y & Z directions 3 個平移——在 X,Y 和 Z 方向
- 3 rotations - about X, Y & Z axes 3 個旋轉——關於 X,Y 和 Z 軸
- The order of the operations matters 這些操作的順序很重要
Affine Transformation Model 仿射轉換模型
- Used for within-subject registration when there is global gross-overall distortion 用於全局粗略失真時的主體內配準
- More typically used as a crude approximation to fully nonrigid transformation. 通常用作完全非剛性轉換的粗略近似。
- Composed of 3 rotation, 3 translations, 3 stretches and 3 shears. 由 3 個旋轉,3 個平移,3 個拉伸和 3 個剪切組成。
- Also a linear transformation – can be represented as a 4x4 matrix 也是線性轉換——可以表示為 4x4 矩陣
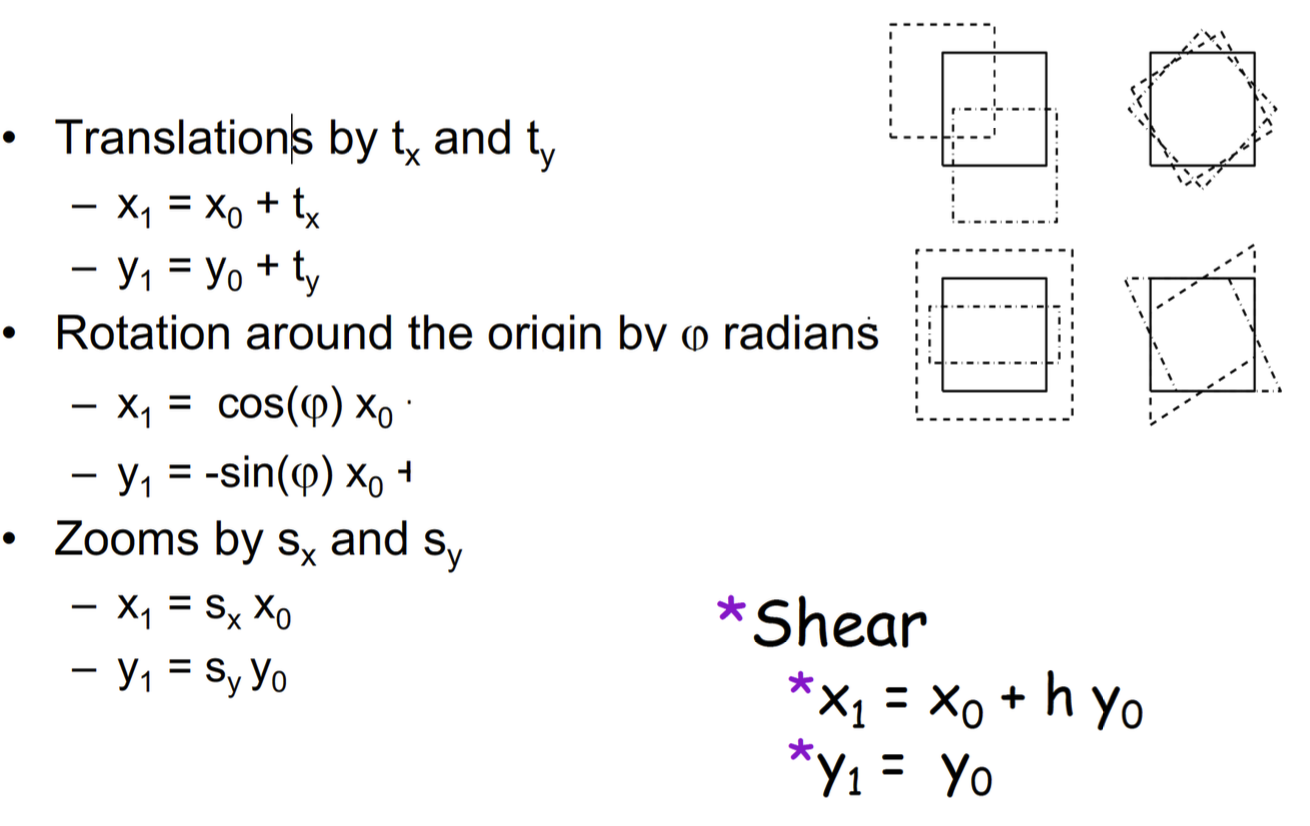
2D Affine Transforms 2D 仿射轉換
Piecewise Affine Transformation Model 分段仿射轉換模型
- Simple extension to fully non-rigid transformation model 簡單的擴展到完全非剛性轉換模型
- Typically use different affine transformation for different parts of the image 通常對圖像的不同部分使用不同的仿射轉換
Non-rigid (elastic) transformation model 非剛性(彈性)轉換模型
- Model the original image as an elastic body acted upon by two types of forces 模擬原始圖像作為一個彈性體受到兩種力的影響
- External forces drive deformation 外力驅動變形
- Internal forces provide constraints 內力提供製約
Non-rigid (elastic) transformation model 非剛性(彈性)轉換模型
- Needed for inter-subject registration and distortion correction 需要跨主體配準和失真校正
- Non-linear i.e. no matrix representation 非線性,即沒有矩陣表示
- Many different parameterizations e.g. 有很多不同的參數化,例如
- Spline parameterizations (b-splines, thin plate splines) 樣條參數化(b 樣條、薄板樣條)
- General diffeomorphisms (e.g. fluid models) 一般的微分形變形(例如流體模型)
- Truncated basis function expansion methods (Fourier parameterizations) 截斷基函數展開方法(傅立葉參數化)
Similarity Metrics (objective functions) 相似度指標(目標函數)
- Feature-based Methods (i.e. using corners, edges, etc) 特徵基礎方法(即使用拐角,邊緣等)
- Geometric distance between corresponding points (e.g. CPD) 對應點之間的幾何距離(例如 CPD)
- Similarity metric between feature values - Similar curvature, etc 特徵值之間的相似度度量——相似曲率等
Similarity Metrics (objective functions) 相似度指標(目標函數)
- Intensity-based Methods (i.e. using image values) 強度基礎方法(即使用圖像值)
- Mean Squared Difference / Sum of Squared Differences 均方差/平方差和
- Only valid for same modality with properly normalized intensities 只適用於同一模態的正確標準化強度
- Mutual Information 互信息
- A metric which maximizes the clustering of the joint histogram. 一個指標,最大化聚類的聯合直方圖。
- Normalized Cross-Correlation 正規化互相關
- Allows for linear relationship between the intensities of the two images 允許兩個圖像的強度之間的線性關係
- Mean Squared Difference / Sum of Squared Differences 均方差/平方差和
Mean-squared Difference (MSD) / Sum of Squared Differences (SSD) 均方差(MSD)/平方差和(SSD)
- Minimising MSD / SSD works for intra-modal and intra-subject registration (realignment) 最小化 MSD/SSD 適用於內模式和內主體配準(重新對齊)
- Simple relationship between intensities in one image, versus those in the other image 一個圖像中強度與另一個圖像中強度之間的簡單關係

Mutual Information 互信息
- Algorithms for maximising mutual information (between intensities) have been some of the most popular for medical image registration to date. 用於最大化互信息(強度)的算法至今已成為醫學影像配準的最受歡迎的方法之一。
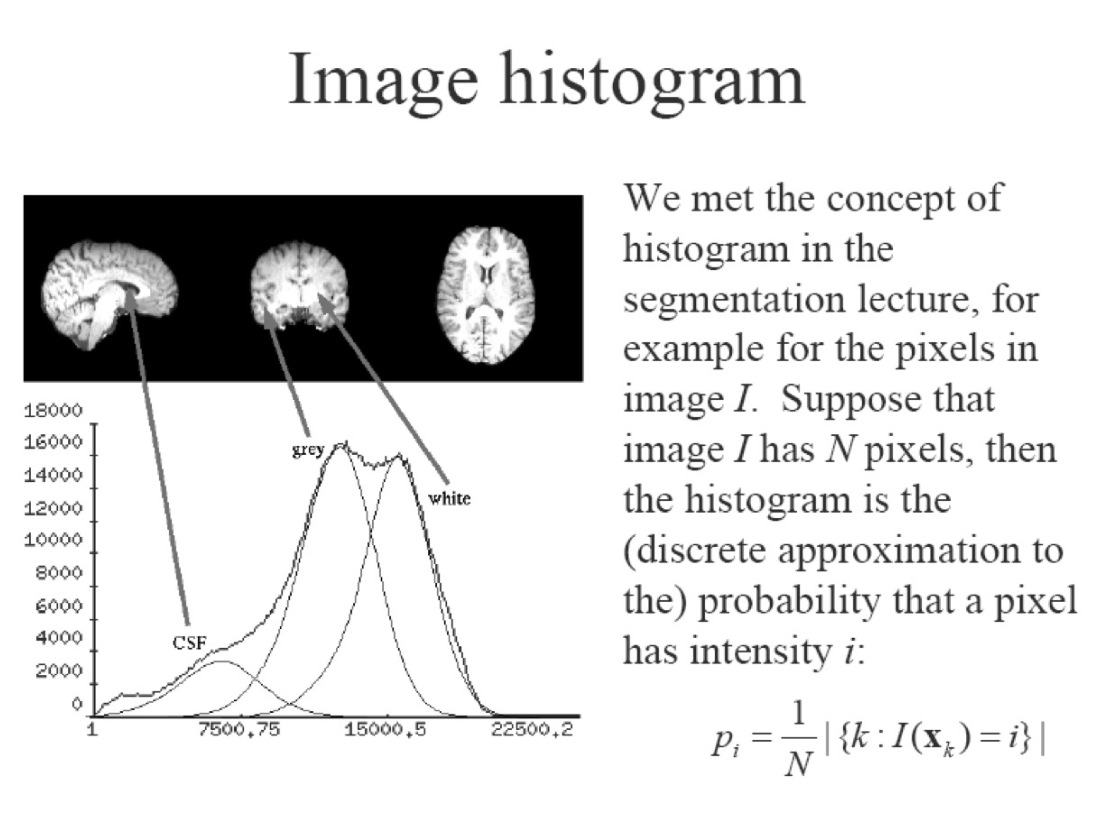
p i= probability of pixel having value i (from image histogram) p i=像素具有值 i 的概率(從圖像直方圖)
Mutual Information 互信息