Genetic and Evolutionary Algorithms 遺傳演算法
Evolution is amazing
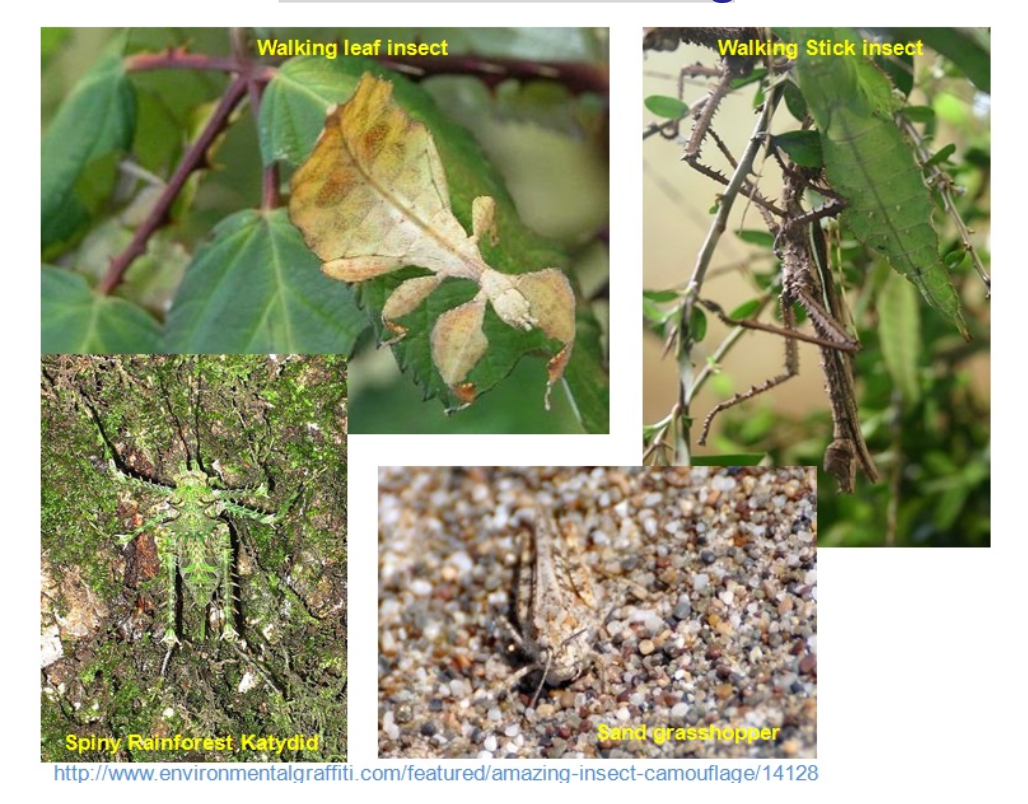

How evolution works in nature? 進化是如何在自然中發生的?
Evolution: change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. 進化:生物種群的遺傳特徵在連續幾代中的變化。
- Heritable characteristics or heritable traits 可遺傳的特徵或可遺傳的特徵
- Example: the colour of your eyes are passed from one generation to the next via DNA 你眼睛的顏色通過 DNA 代代相傳
- DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, a molecule that encodes genetic information in living organisms. DNA 是一種分子,它在生物體中編碼遺傳信息。
- Change or genetic variation comes from: 變化或遺傳變異來自:
- Mutations: changes in the DNA sequence, which may or may not be inherited by the offspring. 突變:DNA 序列的變化,可能會或可能不會被後代繼承。
- Crossover: reshuffling of genes through sexual reproduction and migration between populations 交配:通過性生殖和人口間的迁移重新排列基因
- Heritable characteristics or heritable traits 可遺傳的特徵或可遺傳的特徵
Driving force of evolution: natural selection - survival of the fittest 自然選擇是進化的驅動力:生存的適者
- Genetic variations that enhance survival and reproduction become and remain more common in successive generations of a population. 促進生存和繁殖的遺傳變異在人口的連續幾代中變得更加普遍。
Evolution in Nature 自然中的進化
What evolution taught us 進化教會了我們什麼
- Living species are reproductions of earlier species with genetic variations 現存物種是具有遺傳變異的早期物種的複製品
- Evolution is driven by natural selection - survival of the fittest 進化是由自然選擇驅動的:生存的適者
- Question: How you map the relationship between evolution to optimisation? 如何將進化與最佳化之間的關係映射?
- Fitness → ? in optimisation 适应性 → ?在最佳化中
- Individuals of a specie → ? in optimisation 物種的個體 → ?在最佳化中
What are Evolutionary Algorithms? 什麼是遺傳演算法?
- Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs): a subset of metaheuristic algorithm inspired by biological evolution, which include Genetic Algorithms, Evolutionary Programming, Evolution Strategies, Differential Evolution. 遺傳演算法(EAs)是一個元演算法的子集,受生物進化的啟發,包括遺傳算法,演化式編程,演化策略,差分進化。
- Essentially a kind of stochastic local search optimisation algorithm 基本上是一種隨機局部搜索最佳化算法
- Evolutionary Algorithms ∈ Metaheuristics ∈ Heuristic algorithms ∈ Stochastic Local Search algorithm ∈ Search and enumeration algorithms 遺傳演算法 ∈ 元演算法 ∈ 启發式算法 ∈ 隨機局部搜索算法 ∈ 搜索和枚舉算法
- Distinct characteristic of EAs: 獨特的特徵:
- Population based: generate, maintain and optimise a population of candidate solutions 人口基礎:生成,維護和最佳化一個候選解決方案的人口
Generic Evolutionary Algorithm 通用遺傳演算法

Building blocks of Evolutionary Algorithms 遺傳演算法的組成部分
- An Evolutionary Algorithms consists of: 遺傳演算法由以下部分組成:
- representation: each solution is called an individual or a chromosome 代表:每個解決方案都被稱為個體或染色體
- fitness (objective) function: to evaluate solutions 适应性(目標)函數:評估解決方案
- variation operators: mutation and crossover 變異算子:突變和交叉
- selection and reproduction : survival of the fittest 選擇和繁殖:生存的適者
- Optimisation: finding global optimum is about the balance of exploration and exploitation 最佳化:找到全局最佳值是關於探索和開發的平衡
- Question: How EAs achieve the balance of exploration and exploitation? 如何使遺傳演算法實現探索和開發的平衡?
- Variation operators → exploration or exploitation? 變異算子 → 探索或開發?
- Selection and reproduction → exploration or exploitation ? 選擇和繁殖 → 探索或開發?
- In order to apply an EA to a problem, you need: 要將遺傳演算法應用於問題,您需要:
- A suitable representation of solutions to the problem 一個適合的解決方案的表示
- A way to evaluate solutions: fitness (objective) function 一種評估解決方案的方法:适应性(目標)函數
- A way to explore the space of solutions: variation operators 一種探索解決方案空間的方法:變異算子
- A way to guide the algorithm to find better solutions (exploitation): selection and reproduction 一種指導算法找到更好的解決方案(開發)的方法:選擇和繁殖
Different EAs for optimisation 不同的遺傳演算法用於最佳化
- Genetic algorithm (GA) 遺傳算法
- Most popular type of EA invented by John Holland in 1970s 最受歡迎的 EA 類型由 John Holland 在 1970 年代發明
- Representation: strings of numbers, traditionally binary 數字的字符串,傳統上是二進制字符串
- Variation operators: crossover (recombination) and/or mutation 交叉(重組)和/或突變
- Evolution strategy (ES) 演化策略
- Invented by Ingo Rechenberg and Hans-Paul Schwefel in 1970s 由 Ingo Rechenberg 和 Hans-Paul Schwefel 在 1970 年代發明
- Representation: vectors of real numbers 實數向量的表示
- Variation operators: mutation, typically self-adaptive mutation. 突變,通常是自適應突變
- Evolutionary programming: similar to ES 演化式編程:類似於 ES
- Differential evolution: similar to ES 差分進化:類似於 ES
A more close look at Genetic Algorithm 遺傳算法的更深入的研究
- Genotype 基因型 = Encoded solution 編碼解決方案
- Chromosome 染色體 = Binary string 二進制字符串
- Gene 基因 = Bit 位元
- Allele 等位基因 = 0/1
- Phenotype 表型 = Decoded solution 解碼解決方案
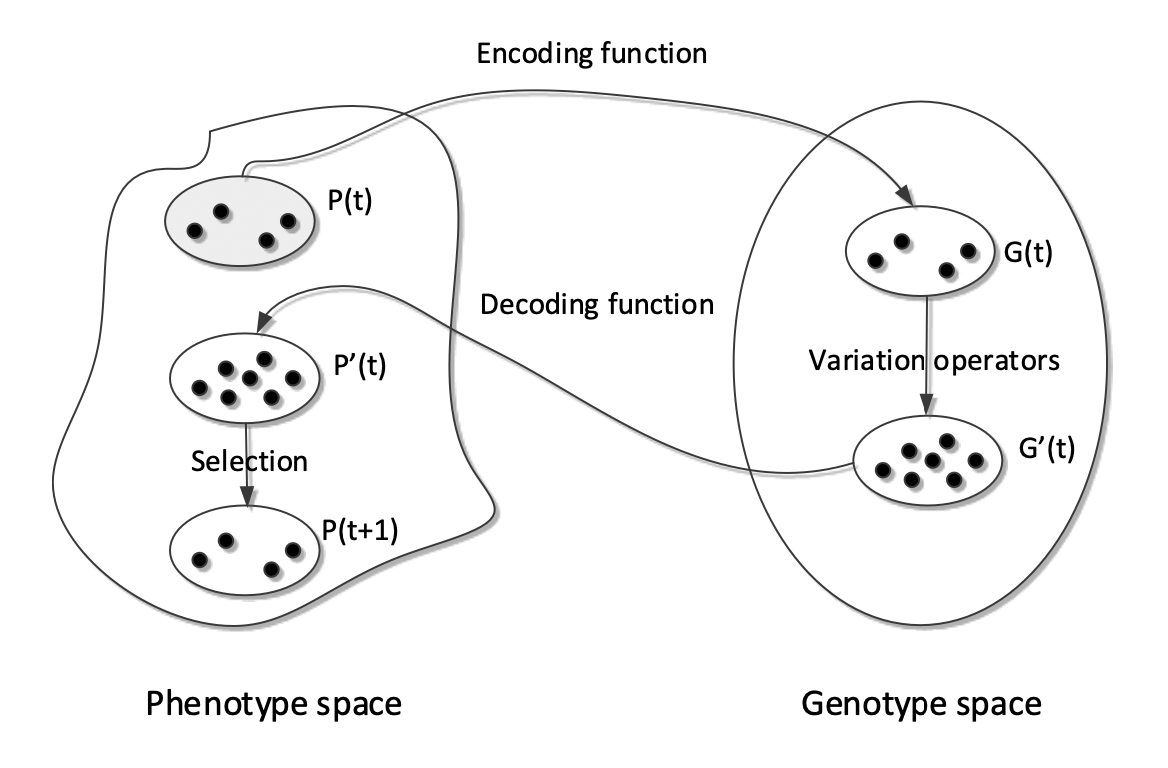
Representation 表示
- Representation: a way to represent (encode) solutions to a problem 代表:一種表示(編碼)問題解決方案的方法
- Suppose we have a optimisation problem, of which the fitness (objective) function is f(x), where x is the solutions. In EAs: 假設我們有一個最佳化問題,其適應性(目標)函數為 f(x),其中 x 是解決方案。在遺傳演算法中:
- Solutions x is called phenotypes 表型
- We encode the solutions using some form of representation, e.g., binary strings (explain later) 我們使用某種形式的表示來編碼解決方案,例如二進制字符串(稍後解釋)
- The representations of solutions is called genotypes 基因型
- Variation operators act on genotypes (bit strings) 變異算子作用於基因型(位元組字符串)
- Genotypes are decoded into phenotypes (solution) x Phenotypes are evaluated using fitness function 基因型被解碼為表型(解決方案)x 表型使用適應性函數 进行評估
- Decoding and encoding functions map phenotypes and genotypes to each other 解碼和編碼函數將表型和基因型映射到彼此
- Search space of solutions is the set of genotypes and phenotypes 解決方案的搜索空間是基因型和表型的集合
- The selection of representation depends on the problem at hand. 選擇表示取決於手頭的問題。
- We have the following choices: 我們有以下選擇:
- Binary representation 二進制表示
- Real number representation 實數表示
- Random key representation 隨機鍵表示
- Permutation representation: suitable for TSP 啟發式表示:適合 TSP 問題
- Other problem specific representations 其他特定問題的表示
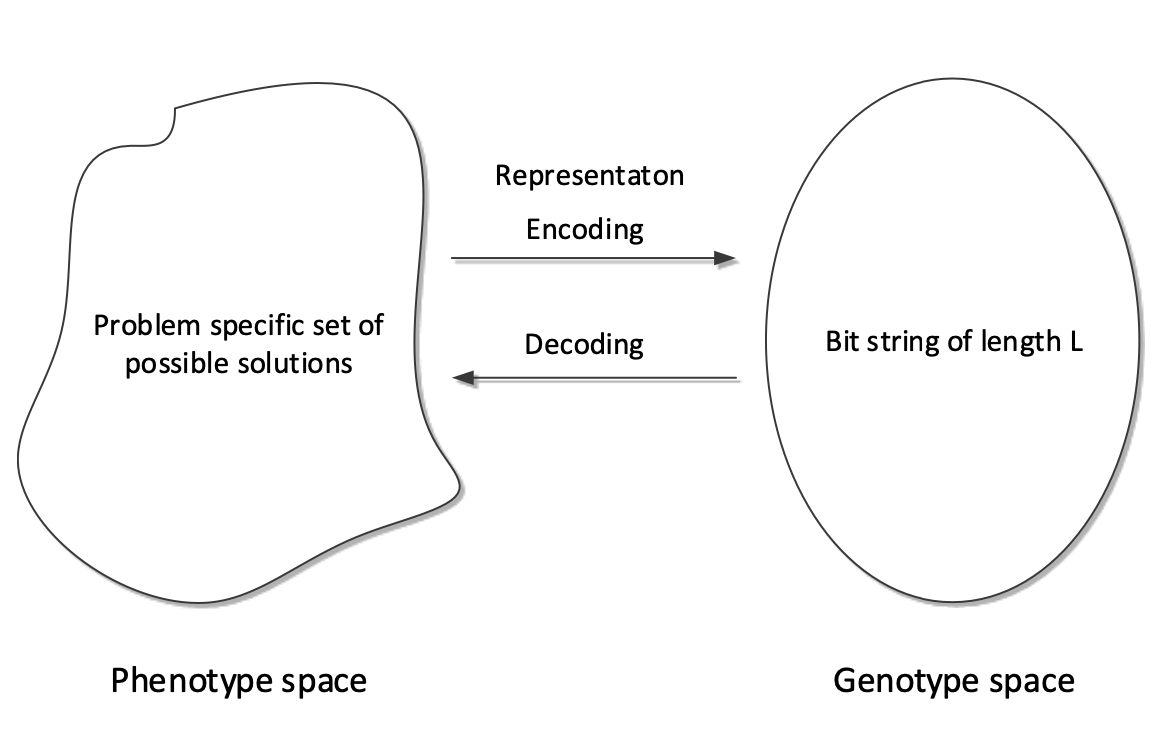
Representation: process of encoding and decoding 表示:編碼和解碼的過程
Binary Representation 二進制表示
- Traditionally was the most popular representation used in Genetic Algorithms 傳統上是遺傳算法中最受歡迎的表示
- Represent an individual (solution) as a bit string of length 將個體(解決方案)表示為長度為 的位元組字符串
- Map phenotypes (solutions) to by encoding function (e.g., binary representation of real numbers) 通過編碼函數(例如,實數的二進制表示)將表型(解決方案)映射到
- Map genotypes (bit strings ) to phenotypes (solutions) by decoding function (e.g., binary to real number) 通過解碼函數(例如,二進制到實數)將基因型(位元組字符串 )映射到表型(解決方案)
Decoding function 解碼函數
- Using a bit string to represent a binary or an integer solution is trivial 用位元組字符串來表示二進制或整數解決方案是微不足道的
- Question: given an optimisation problem with n continuous variables, e.g., , how to represent them using a bit string of length L, e.g., ?問題:給定一個具有 n 個連續變量的最佳化問題,例如,,如何使用長度為 L 的位元組字符串來表示它們,例如, ?
- Note: usually each continuous variable have a interval bound, e.g., 通常每個連續變量都有一個區間界限,例如
- Divide into n segments of equal length
- Decode each segment into an integer , and
- Apply decoding function , i.e., map the integer linearly into the interval bound
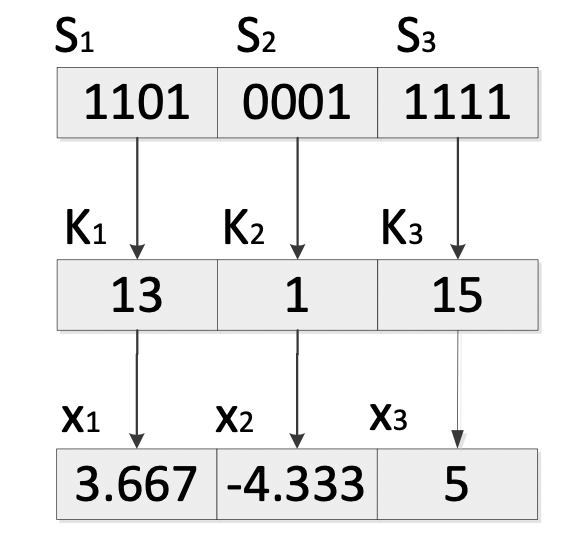
Decoding function: Example 解碼函數:示例
- Assume and
- Use a bit string of , therefore bits segment
Building blocks of Evolutionary Algorithms 进化算法的基本组件
- In order to apply an EC to a problem, you need: 要將 EC 應用於問題,您需要:
- A suitable representation of solutions to the problem X 一個適合的解決方案表示
- A way to evaluate solutions: fitness (objective) function X 一種評估解決方案的方法:適應度(目標)函數
- A way to explore the space of solutions: variation operators X 一種探索解決方案空間的方法:變異算子
- A way to guide the algorithm to find better solutions (exploitation): selection and reproduction operators X 一種指導算法找到更好的解決方案的方法(利用):選擇和繁殖算子
Mutation 變異
- Mutation: flip each bit with a probability pm, called mutation rate 變異:以概率 pm 翻轉每個位元,稱為變異率
- The standard mutation rate is but can be 一般的變異率是 ,但可以是
- Example:
- Parent: 00101011
- After Mutation: 01101001
- If mutation rate is small, mutation can be seen as creating a small random perturbation on the parent genotype 小變異率可以看作是在父代基因型上創建一個小的隨機扰動
- The mutated offspring is largely similar to its parent, so will stay near (in terms of Hamming Distance) the parent in the genotype search space 變異後的後代與其父代相似,因此在基因型搜索空間中會保持在父代附近(就 Hamming 距離而言)
- Together with selection what mutation actually does is stochastic local search: it exploit current good solutions by randomly explore the search space around them 通過選擇,變異實際上執行的是隨機局部搜索:它通過隨機探索當前良好解決方案周圍的搜索空間來利用當前良好的解決方案
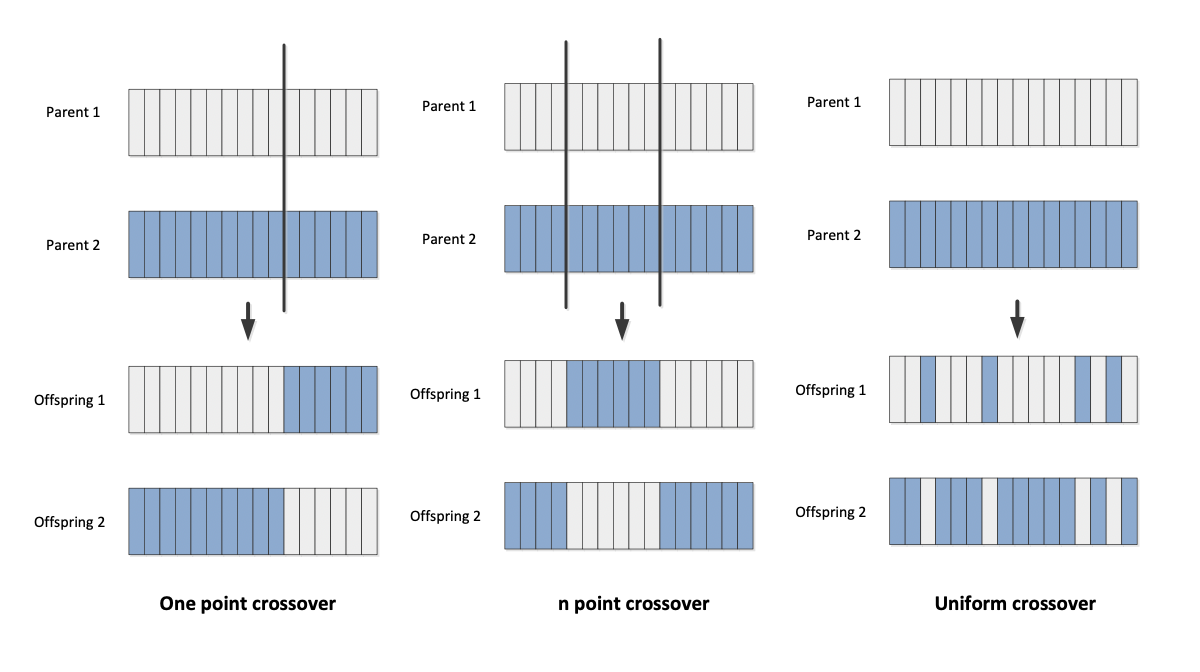
Crossover 交叉
- Randomly select two parents with probability for crossover 以概率 隨機選擇兩個父代進行交叉
- 1-point crossover: 1 點交叉:
- select a single crossover point on two strings, swap the data beyond that point in both strings. 在兩個字符串上選擇一個交叉點,交換該點之後的數據在兩個字符串中。
- n-point crossover: n 點交叉:
- Select multiple crossover points on two strings, 在兩個字符串上 選擇多個交叉點,
- Split strings into parts using those points 將字符串使用這些點分割成多個部分
- Alternating between the two parents and then glue parts 在兩個父母之間交替,然後粘合零件
- Uniform crossover: 均勻交叉:
- For each : toss a coin 對於每個 :拋硬幣
- If 'head': copy bit i from parent 1 to offspring 1, parent 2 to offspring 2 如果是"正面",則從父代 1 复制位元 i 到後代 1,從父代 2 到後代 2
- If 'tail': copy bit i from parent 1 to offspring 2, parent 2 to offspring 1 如果是"反面",則從父代 1 复制位元 i 到後代 2,從父代 2 到後代 1
Crossover illustration 交叉說明
Conclusion 結論
- Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs): metaheuristics optimisation algorithm or stochastic local search algorithm 进化算法(EAs):元启发式优化算法或随机局部搜索算法
- One feature of EAs: population-based
- Genetic Algorithm traditionally used binary string as representation: might not be the best problem representation 一般使用二進制字符串作為表示:可能不是最好的問題表示
- Two essential mechanisms: variation and selection 二個基本機制:變異和選擇
- Variation operators: introduce randomness to explore the space of solutions 變異算子:引入隨機性來探索解決方案空間
- Selection and reproduction: exploit current good solutions to find better solutions 選擇和繁殖:利用當前良好的解決方案來找到更好的解決方案
- Genetic Algorithm is the most popular EA 遺傳算法是最流行的 EA
- GA traditionally uses binary string to represent the solution (encoding): might not be the best problem representation 一般使用二進制字符串來表示解決方案(編碼):可能不是最好的問題表示