Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) 尺度不變特徵變換
Group Activity 集體活動
Given this noisy image, design the best suitable algorithm to detect edges. 給定這個嘈雜的圖像,設計最合適的算法來檢測邊緣。
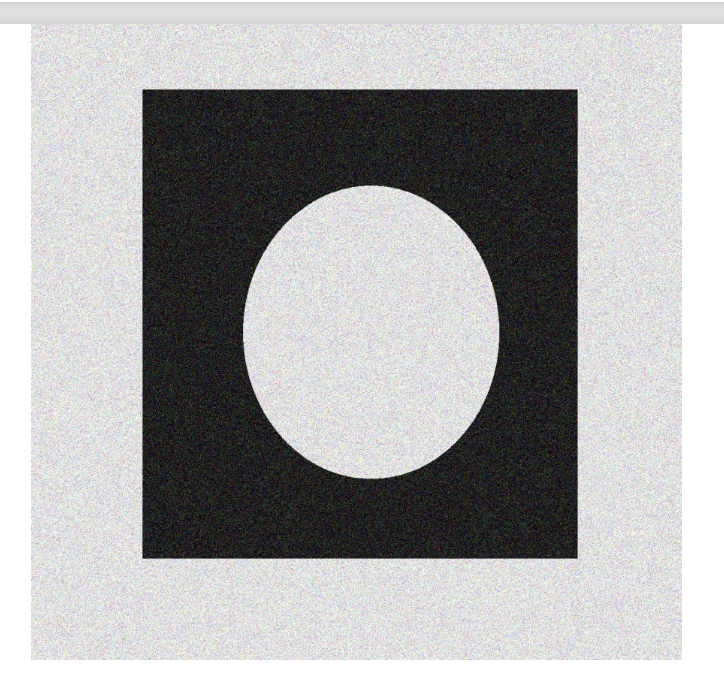
Given the calculated edges, how would you quantify accuracy? 給定計算出的邊緣,你如何量化準確性?

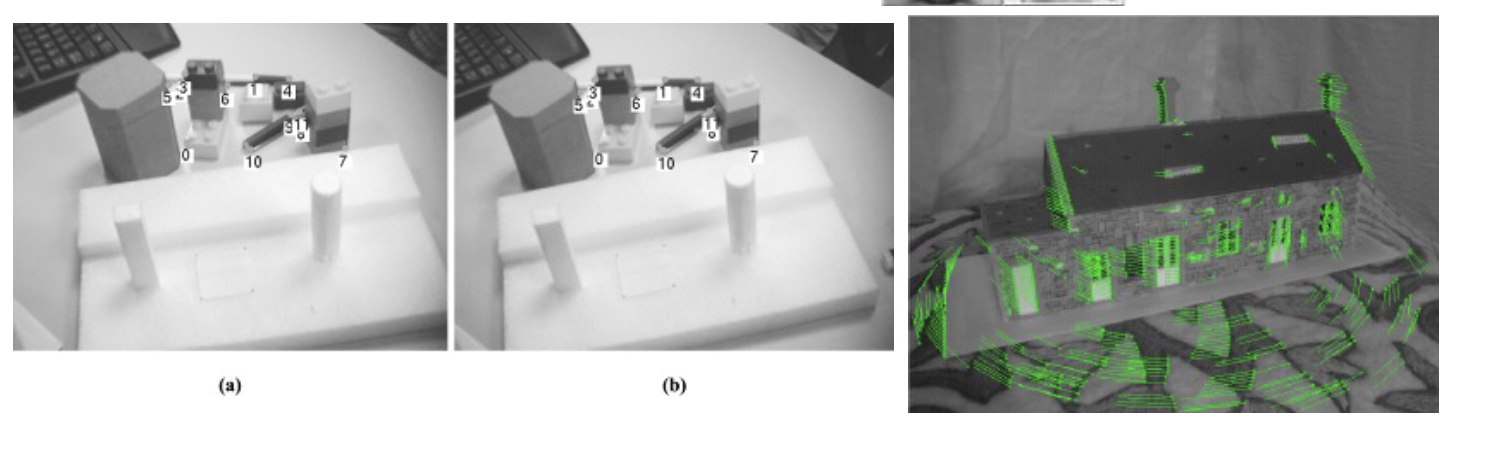
Why do we care about matching features? 我們為什麼要關心匹配特徵?
- Object Recognition 物體識別
- Wide baseline matching (stereo) 大幅度匹配(立體)
- Given any two images, estimate the fundamental matrix and a set of matched interest points. 給定任何兩個圖像,估計基礎矩陣和一組匹配的關注點。
- Tracking 跟蹤

We want invariance!!! 我們想要不變性!!!
- Good features should be robust to all sorts of nastiness that can occur between images. 好的特徵應該能夠抵抗圖像之間可能發生的各種惡劣情況。
Types of invariance 不變性的類型
- Illumination 照明
- Scale 尺度
- Rotation 旋轉
- Affine 仿射
- Full Perspective 全景
How to achieve illumination invariance 如何實現照明不變性
- The easy way (normalized) 簡單的方法(正規化)
- Difference based metrics (sift) 差異度量(sift)
How to achieve scale invariance 如何實現尺度不變性
- Pyramids 金字塔
- Divide width and height by 2 將寬度和高度除以 2
- Take average of 4 pixels for each pixel (or Gaussian blur) 對每個像素取 4 像素的平均值(或高斯模糊)
- Repeat until image is tiny 重複直到圖像很小
- Run filter over each size image and hope its robust 對每個大小的圖像運行過濾器並希望它的魯棒性

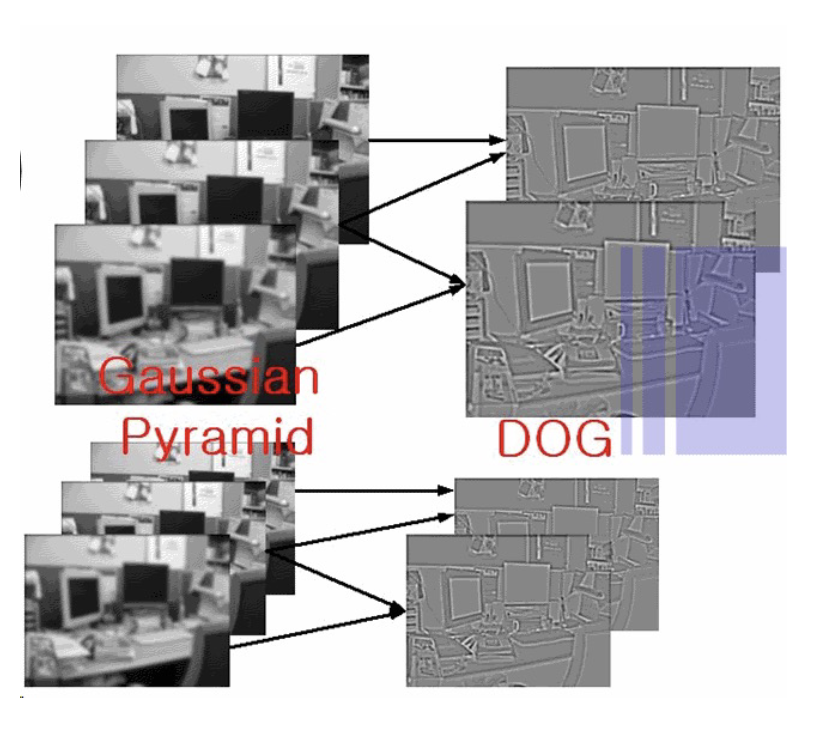
- Scale Space (DOG method) 尺度空間(DOG 方法)
- Pyramid but fill gaps with blurred images 金字塔但用模糊的圖像填補空隙
- Like having a nice linear scaling without the expense 就像有一個很好的線性縮放而不需要花費
- Take features from differences of these images 從這些圖像的差異中提取特徵
- If the feature is repeatably present in between Difference of Gaussians it is Scale Invariant and we should keep it. 如果該特徵在不同的高斯差異中可重複出現,則該特徵是尺度不變的,我們應該保留它。
Differences Of Gaussians (DOG) 高斯差異
Rotation Invariance 旋轉不變性
- Rotate all features to go the same way in a determined manner 以確定的方式旋轉所有特徵以相同的方式
- Take histogram of Gradient directions 獲取梯度方向的直方圖
- Rotate to most dominant (maybe second if its good enough) 旋轉到最主要的(如果足夠好,可能是第二個)