Human Vision 人類視覺
Retina Processing 視網膜處理
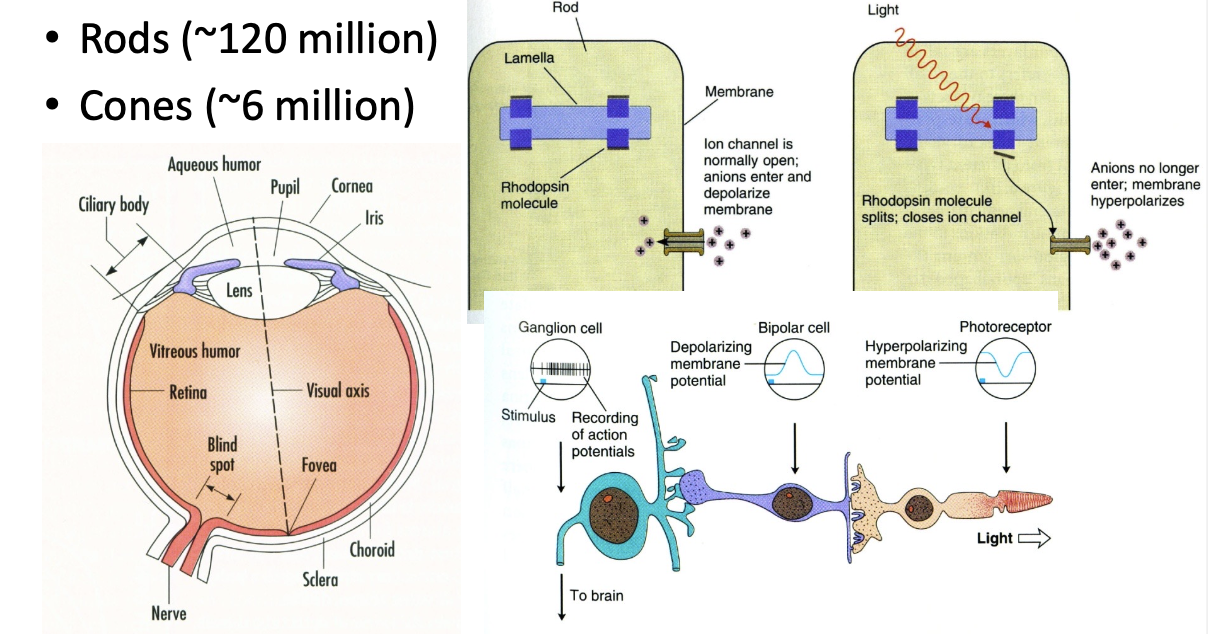
- The retina contains cells that respond to light: 視網膜包含對光有反應的細胞:
- Two types of photorecepetors 兩種類型的光感受器
- Rods (~120 million) 棒子(~ 120000 萬)
- Cones (~6 million) 棱錐(~ 600 萬)
- Two types of photorecepetors 兩種類型的光感受器
Blind Spot Test 盲點測試

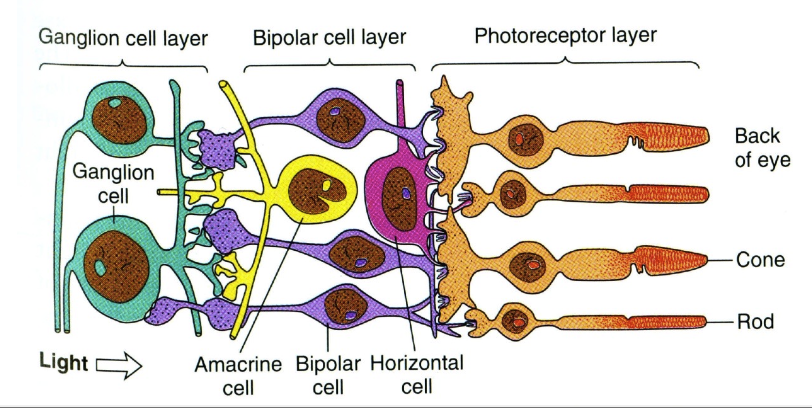
Rods and Cones 棒子和棱錐
- Rods
- ~120 m
- Extremely sensitive photosensor
- Respond to a single photon
- Poor spatial resolution as they converge to same neuron within retina 空間分辨率差,因為它們會聚到視網膜內的同一個神經元
- Cones
- ~6 m
- Active at higher light levels
- Higher resolution as Signal processed by several neurons
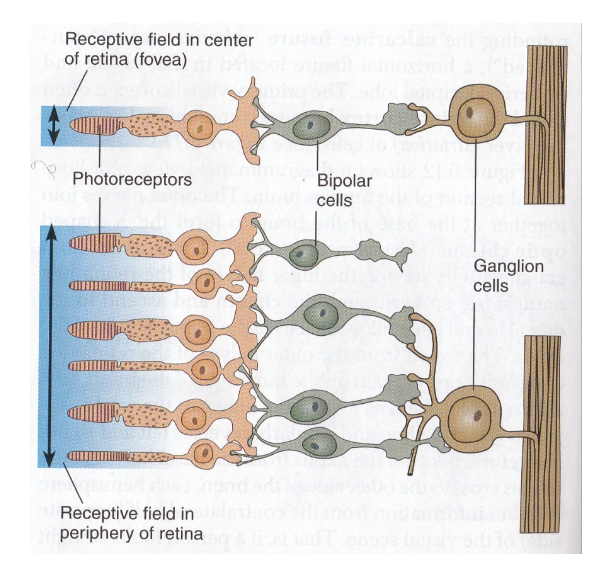
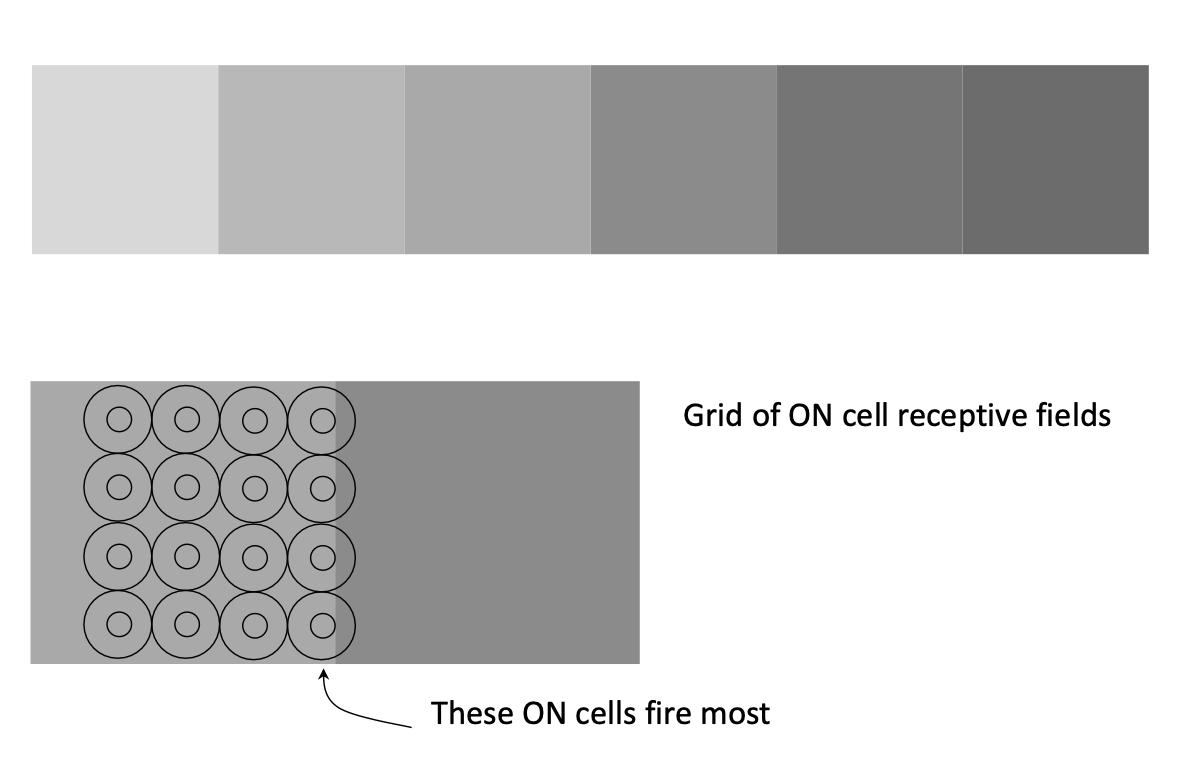
Receptive Field 感受野
- Receptive field is the area on which light must fall for neuron to be stimulated. 感受野是光必須落在的區域,以刺激神經元。
- Note difference between centre and periphery of field (centre is more sensitive) 注意感受野的中心和周圍的區域(中心更敏感)
- As early as 1938, frogs were seen to have different types of ganglion cells 早在 1938 年,人們就發現青蛙有不同類型的神經節細胞
- Using Cats, (electrical recordings from ganglion cells) it was seen that receptive field contains a circular centre surrounded by a ring of inhibition. 使用貓,(從神經節細胞的電流記錄)發現感受野包含一個圓形中心,周圍是一圈抑制。
Ganglion cells 神經節細胞
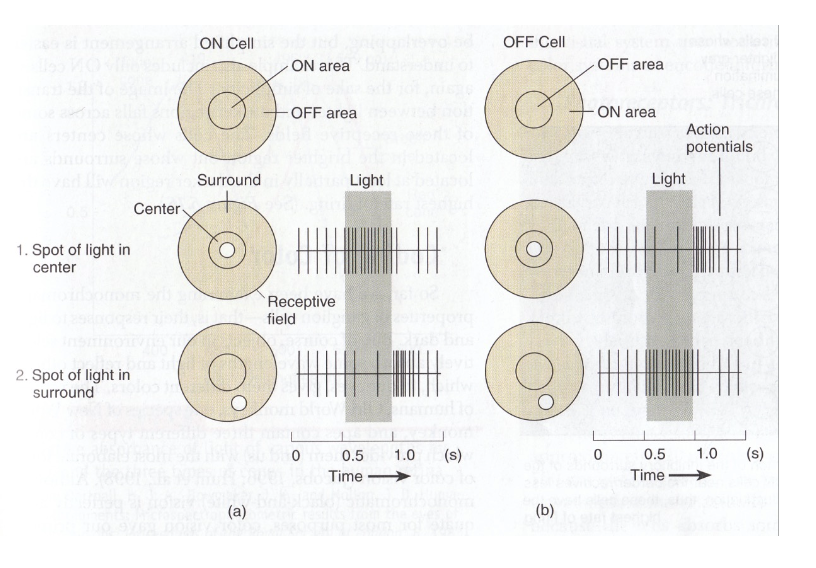
- Two types: "on-center" and "off-center". 兩種類型:"on-center"和"off-center"。
- On-center: stimulated when the center of its receptive field is exposed to light, and is inhibited when the surround is exposed to light. 中心被光照射時刺激,周圍被光照射時抑制。
- Off-center cells have just the opposite reaction to light. off-center 細胞對光的反應正好相反。
- Allows ganglion cells to transmit information not merely about whether photoreceptor cells are firing (Photoreceptors do not actually fire action potentials), but also about the differences in firing rates of cells in the center and surround. 允許神經節細胞傳輸不僅有關光感受器細胞是否發射的信息(光感受器實際上不會發射動作電位),還有關中心和周圍細胞發射率的差異。
- Allows transmission of information about contrast. 允許傳輸有關對比的信息。
- The size of the receptive field governs the spatial frequency of the information that can be transmitted. 感受野的大小決定了可以傳輸的空間頻率的信息。
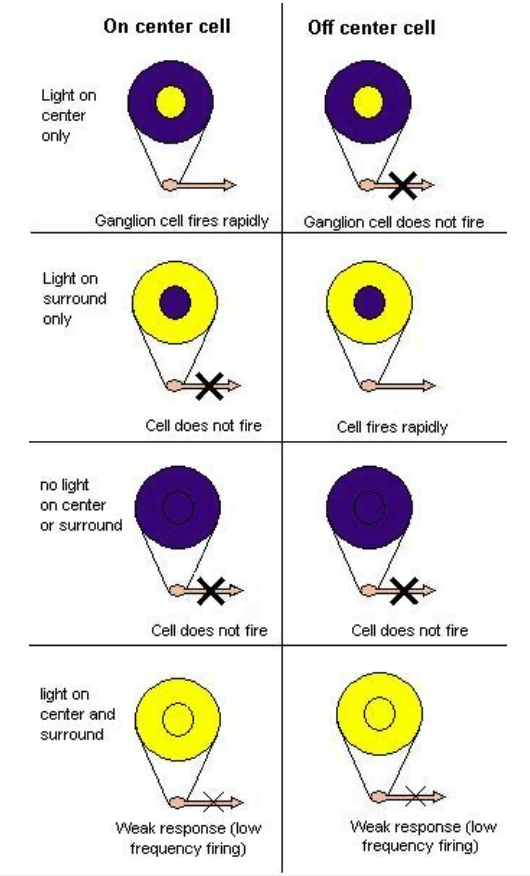
ON/OFF Cells
- Note
- area of stimulation / inhibition 刺激/抑制區域
- Rate of signal firing (rebound) 發射率(反彈)
Enhancement of Contrast 增強對比
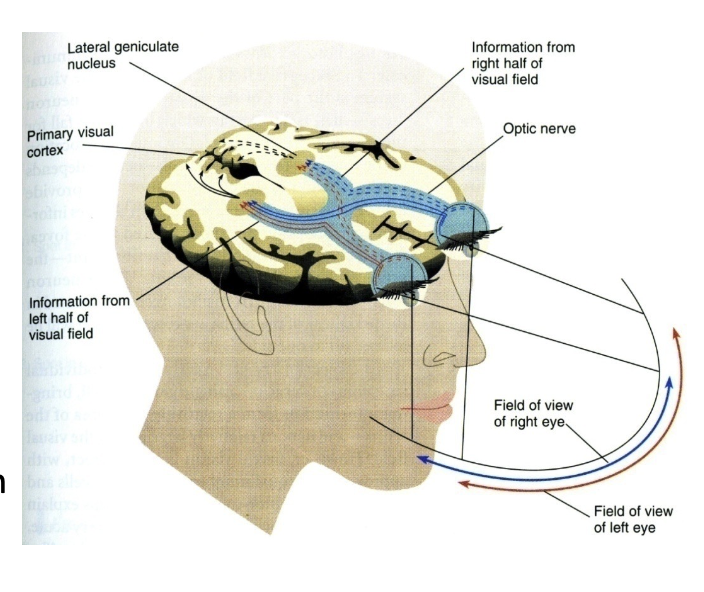
Visual Pathway 視覺通路
- Vision generated by photoreceptors in the retina 視覺由視網膜中的光感受器產生
- The information leaves the eye by way of the optic nerve 信息通過視神經離開眼睛
- There is a partial crossing of axons at the optic chiasm. 有一部分的軸突在視神經交叉處交叉。
- After the chiasm, the axons are called the optic tract. 在交叉處,軸突被稱為視神經。
- The optic tract wraps around the midbrain to get to the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus. 視神經繞過中腦包到樞體的外側基質核(LGN)。
- The LGN axons fan out through the deep white matter of the brain and ultimately travel to primary visual cortex, at the back of the brain. LGN 軸突通過腦的深白質,最終到達腦後部的主視覺皮質。
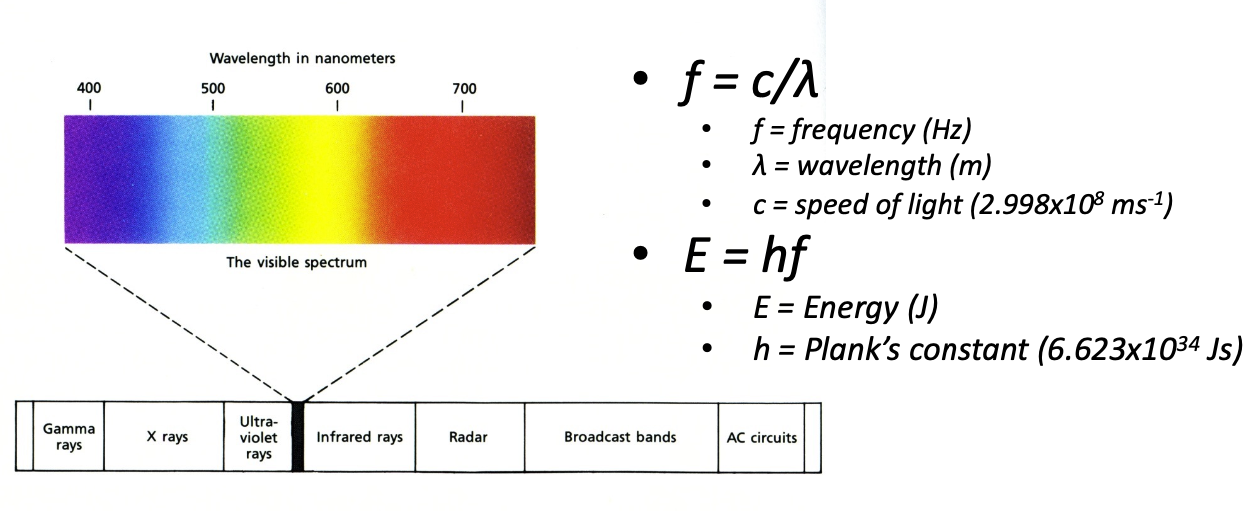
Visible Light 可見光
- Humans perceive electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths 380-760nm (1 nm = 10-^9 m) 人類感知的電磁波長度為 380-760nm(1 nm = 10-^9 m)
Colour 色彩
- Objects selectively absorb some wavelengths (colours) and reflect others 被選擇性地吸收某些波長(顏色)的物體,並反射其他波長。
- Human retinas contain three different kinds of cones to provide very elaborate form of vision 人類視網膜包含三種不同類型的錐體,以提供非常精緻的視覺形式。
- Gives ability to distinguish different forms of same objects (e.g. apples) 使人能夠區別同一物體的不同形式(例如蘋果)。
- Fruits 水果
- Camouflage is effective only if the background is similar to the object. 伪裝只有在背景與物體相似時才有效。
Colour mixing 色彩混合
- Many forms of colour vision proposed 過去提出了許多種類的色彩視覺
- Until recently some hard to disapprove 過去有些難以否認
- 1802: Proposed that the eye has three different types of receptors, each sensitive to a single hue (Young, a British physicist) 提出眼睛有三種不同類型的感受器,每種感受器對單一色調敏感(Young,一位英國物理學家)。
- By the fact that any colour can be produced by appropriate mixing of the three primary colours. 通過任何顏色都可以通過適當混合三種原色而產生。
- This became known as Trichromatic (three-colour) theory. 這稱為 Trichromatic(三色)理論。
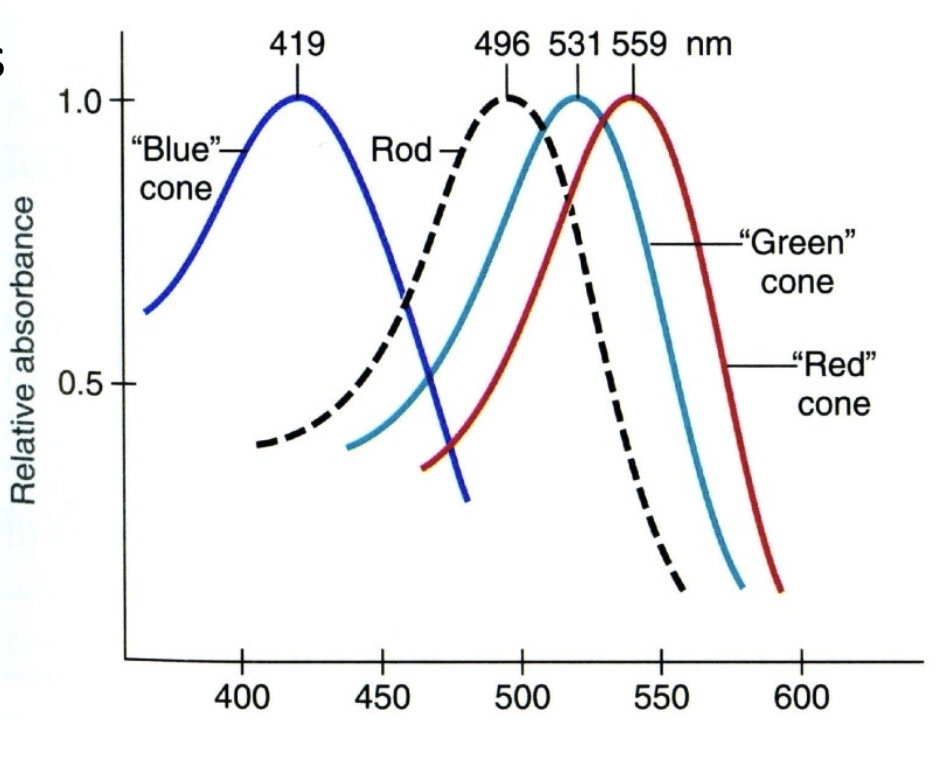
Trichromatic Coding 三色編碼
Retina contains approximately equal numbers of red and green cones, but only 8% are blue cones 視網膜包含大約相等數量的紅色和綠色錐體,但只有 8% 是藍色錐體。
Explains
- How we discriminate wavelengths 2nm in difference 我們如何區分相差 2nm 的波長
- How we can match a mixture of wavelengths to a single colour 我們如何將波長混合匹配到單一顏色
- Some types of colour blindness 一些類型的色盲
Does not account for colour blending: 不能解釋顏色混合:
- Some colour blend while others don't! 有些顏色混合,而其他顏色則不會!
- One can imaging Bluish-green or Yellowish-green, But NOT Greenish- red or Bluish-yellow! 人們可以想像藍綠色或黃綠色,但不會想像綠紅色或藍黃色!
Colour mixing 色彩混合
- Many forms of colour vision proposed 過去提出了許多種類的色彩視覺
- Until recently some hard to disapprove 過去有些難以否認
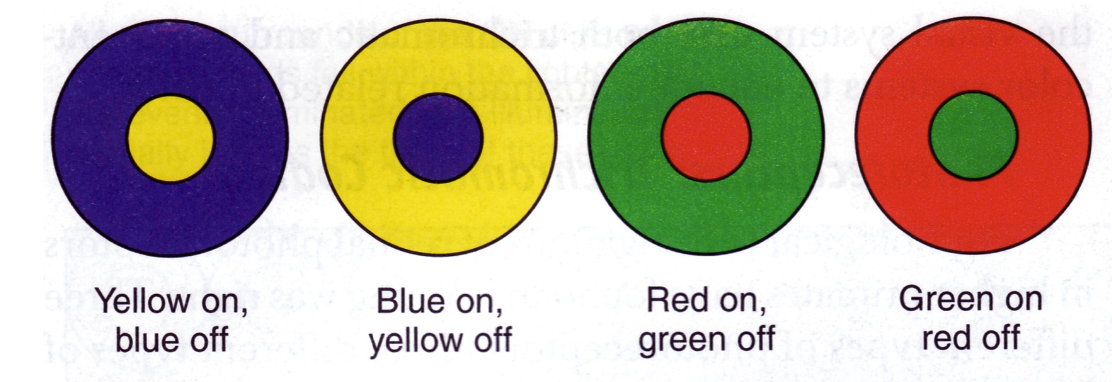
- 1930s: Hering (German Physiologist) suggested colour may be represented in visual system as 'opponent colours' 1930 年代:Hering(德國生理學家)建議顏色在視覺系統中可以表示為"對立色"
- Yellow, Blue, Red and Green - Primary colours 主要顏色
- Trichromatic theory cannot explain why yellow is a primary colour 三色理論不能解釋為什麼黃色是主要顏色
Opponent Process Coding 對立過程編碼
- Yellow, Blue, Red and Green – Primary colours 主要顏色
- Trichromatic theory cannot explain why yellow is a primary colour 三色理論不能解釋為什麼黃色是主要顏色
- Also some colours blend and others do not! 也有一些顏色混合,而其他顏色則不會!
- Bluish green, yellowish green, orange (red and yellow), purple (red and blue) OK 藍綠色,黃綠色,橙色(紅色和黃色),紫色(紅色和藍色)OK
- Reddish green?? Bluish Yellow?? 紅綠色??藍黃色??
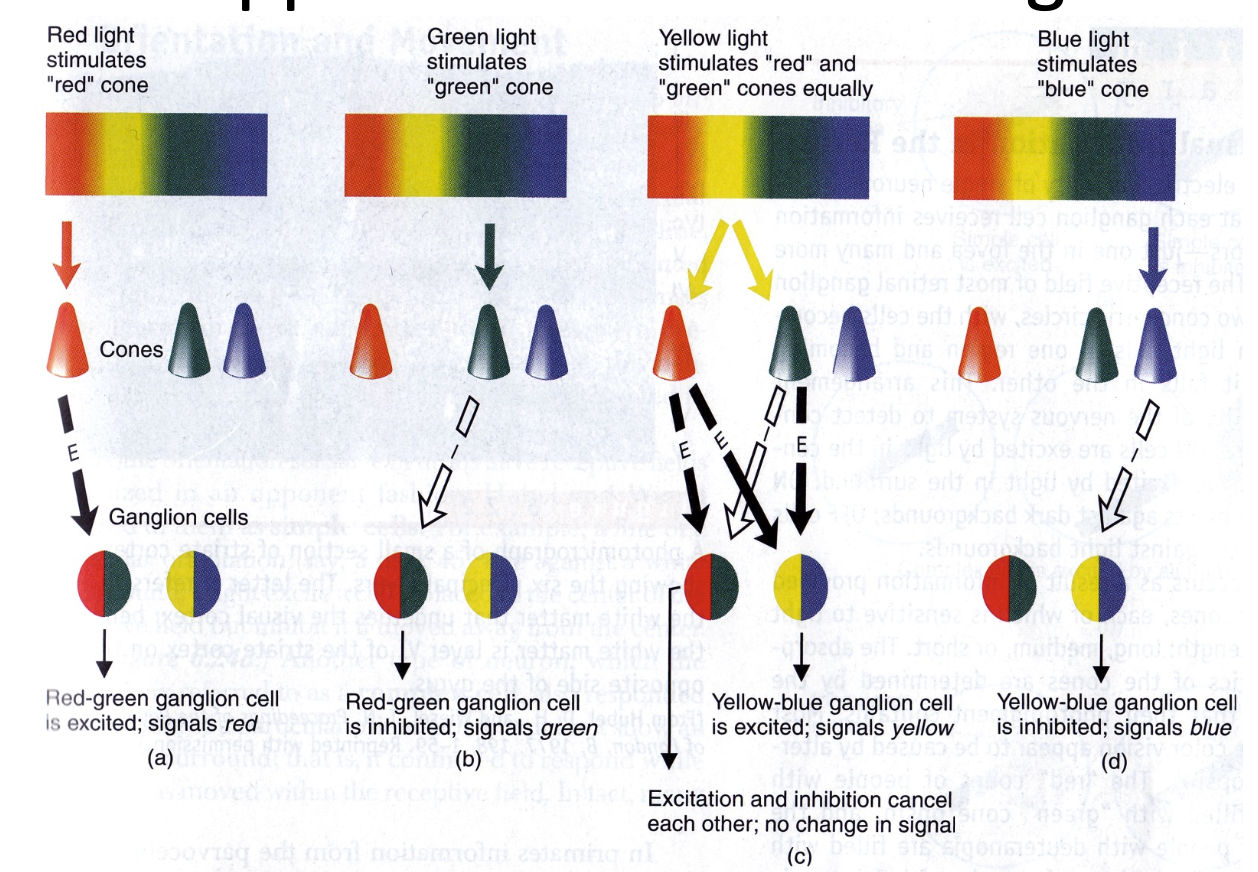
- Opposite to each other 對立彼此
- Neurons respond to pairs of primary colours 神經元對成對的原色作出反應
- Red-Green & Yellow-Blue
- Some respond in centre-surround fashion 有些人以中心環繞方式回應
- Response characteristics determined by appropriate ganglion cells connections 應該由適當的腦幹細胞連接決定回應特性
Opponent Process Coding 對立過程編碼
Reading
- Vicki Bruce, Visual Perception, Chapters 1 - 3
- Neil Carlson, Physiology of Behavior, Chapter 3, "Vision"